Power modulation of electroencephalogram mu and beta frequency depends on perceived level of observed actions
- PMID: 27547498
- PMCID: PMC4980467
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.494
Power modulation of electroencephalogram mu and beta frequency depends on perceived level of observed actions
Abstract
Introduction: The ability to understand actions and intentions of others is of great importance to social relationships and is associated with the mirror neuron system of the human brain. Whether conscious perception of specific actions is necessary to trigger activity in this system, or alternatively whether this response is independent of conscious perception is not known.
Methods: We addressed this issue by rendering videos of right hand movements invisible to conscious perception, and measuring electroencephalogram (EEG) power suppression in the mu (8-13 Hz) and beta (15-25 Hz) range as index corresponding to the magnitude of mirror neuron activity.
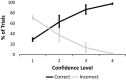
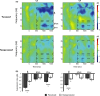
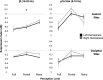
Results: In the beta range over bilateral sensorimotor sites, we find that suppression indices follow the reported perceptual level of subjects with stronger suppression for consciously perceived trials. Furthermore, in the nonperceived trials, oscillation power is significantly suppressed relative to baseline. In the low mu range (8-10 Hz), oscillation power over the left sensorimotor site is significantly more suppressed in the consciously perceived versus nonperceived trials.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the intensity of mirror system responses during action observation decreases with the observers' perception level yet remains significant during observation of invisible actions. Such subliminal activity could help explain phenomena such as covert imitation.
Keywords: Action observation; conscious perception; electroencephalogram; mirror neuron system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of visual orientation on mu suppression in children: a comparative EEG study with adults.J Physiol Anthropol. 2018 Jun 8;37(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40101-018-0175-9. J Physiol Anthropol. 2018. PMID: 29884245 Free PMC article.
-
A study of EEG mu neurofeedback during action observation.Exp Brain Res. 2020 May;238(5):1277-1284. doi: 10.1007/s00221-020-05808-9. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Exp Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32303811
-
Crossmodal Classification of Mu Rhythm Activity during Action Observation and Execution Suggests Specificity to Somatosensory Features of Actions.J Neurosci. 2017 Jun 14;37(24):5936-5947. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3393-16.2017. Epub 2017 May 30. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28559380 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding intentions from actions: Direct perception, inference, and the roles of mirror and mentalizing systems.Conscious Cogn. 2015 Nov;36:426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2015.03.012. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Conscious Cogn. 2015. PMID: 25864592 Review.
-
Perception of robotic actions and the influence of gender.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 31;15:1295279. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1295279. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38356771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imperceptible Somatosensory Single Pulse and Pulse Train Stimulation Oppositely Modulate Mu Rhythm Activity and Perceptual Performance.Cereb Cortex. 2020 Nov 3;30(12):6284-6295. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa185. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 32776096 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Mirror System (MS) Activity in Adults with ASD When Inferring Others' Intentions Using Both TMS and EEG.J Autism Dev Disord. 2018 Jul;48(7):2350-2367. doi: 10.1007/s10803-018-3492-2. J Autism Dev Disord. 2018. PMID: 29453710 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral hemodynamic response during a live action-observation and action-execution task: A fNIRS study.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 13;16(8):e0253788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253788. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34388157 Free PMC article.
-
Toward understanding the neurophysiological basis of peripersonal space: An EEG study on healthy individuals.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 24;14(6):e0218675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218675. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31233542 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity to perception level differentiates two subnetworks within the mirror neuron system.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017 May 1;12(5):861-870. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsx015. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28338793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babiloni, C. , Vecchio F., Bultrini A., Luca Romani G., and Rossini P. M.. 2006. Pre‐ and poststimulus alpha rhythms are related to conscious visual perception: a high‐resolution EEG study. Cereb. Cortex 16:1690–1700. - PubMed
-
- Bazanova, O. M. , and Vernon D.. 2014. Interpreting EEG alpha activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 44:94–110. - PubMed
-
- Caggiano, V. , Fogassi L., Rizzolatti G., Thier P., and Casile A.. 2009. Mirror neurons differentially encode the peripersonal and extrapersonal space of monkeys. Science 324:403–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

