Genomic Integrity Is Favourably Affected by High-Intensity Interval Training in an Animal Model of Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 27547714
- PMCID: PMC4978751
- DOI: 10.1186/s40798-016-0055-y
Genomic Integrity Is Favourably Affected by High-Intensity Interval Training in an Animal Model of Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an irreversible disease that diminishes length and quality of life. Emerging evidence suggests CKD progression and genomic integrity are inversely and causally related. To reduce health complications related to CKD progression, chronic aerobic exercise is often recommended. To date, appraisals of differing modes of exercise, along with postulations regarding the mechanisms responsible for observed effects, are lacking. In order to examine the ability of aerobic exercise to encourage improvements in genomic integrity, we evaluated the effects of 8 weeks of high-intensity interval training (HIIT; 85 % VO2max), low intensity training (LIT; 45-50 % VO2max), and sedentary behaviour (SED), in an animal model of early-stage CKD.
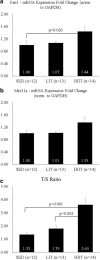
Methods: To assess genomic integrity, we examined kidney-specific messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of genes related to genomic repair and stability: Fan1, Mre11a, and telomere length as measured by T/S ratio.
Results: Following HIIT, mRNA expression of Fan1 was significantly up-regulated, compared to SED (p = 0.026) and T/S ratio was significantly increased, compared to SED (p < 0.001) and LIT (p = 0.002).
Conclusions: Our results suggest that HIIT is superior to SED and LIT as HIIT beneficially influenced the expression of genes related to genomic integrity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Intensity Interval Training Favourably Affects Angiotensinogen mRNA Expression and Markers of Cardiorenal Health in a Rat Model of Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:156584. doi: 10.1155/2015/156584. Epub 2015 May 24. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26090382 Free PMC article.
-
High intensity interval training favourably affects antioxidant and inflammation mRNA expression in early-stage chronic kidney disease.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Dec;89:466-72. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.07.162. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26453919
-
Light-intensity and high-intensity interval training improve cardiometabolic health in rats.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016 Sep;41(9):945-52. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0037. Epub 2016 May 4. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016. PMID: 27523646
-
Effects of different protocols of high intensity interval training for VO2max improvements in adults: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.J Sci Med Sport. 2019 Aug;22(8):941-947. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 29. J Sci Med Sport. 2019. PMID: 30733142
-
Potential Universal Application of High-intensity Interval Training from Athletes and Sports Lovers to Patients.Keio J Med. 2017 Jun 25;66(2):19-24. doi: 10.2302/kjm.2016-0006-IR. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Keio J Med. 2017. PMID: 27498746 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Susceptibility to Chronic Kidney Disease - Some More Pieces for the Heritability Puzzle.Front Genet. 2019 May 31;10:453. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00453. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31214239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous