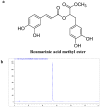
Rosmarinic Acid Methyl Ester Inhibits LPS-Induced NO Production via Suppression of MyD88- Dependent and -Independent Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells
- PMID: 27548124
- PMCID: PMC6274143
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21081083
Rosmarinic Acid Methyl Ester Inhibits LPS-Induced NO Production via Suppression of MyD88- Dependent and -Independent Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells
Abstract
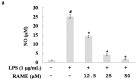
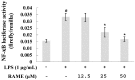
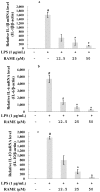
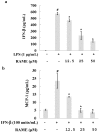
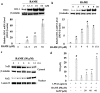
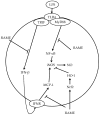
In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of rosmarinic acid methyl ester (RAME) isolated from a mutant cultivar of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britton. We found that RAME inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production, with an IC50 of 14.25 µM, in RAW 264.7 cells. RAME inhibited the LPS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, interferon-β, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Moreover, RAME suppressed the activation of nuclear factor kappa B. These results suggest that the downregulation of iNOS expression by RAME was due to myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88)-dependent and -independent pathways. Furthermore, RAME induced the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) through activation of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2. Treatment with tin protoporphyrin, an inhibitor of HO-1, reversed the RAME-induced suppression of NO production. Taken together, RAME isolated from P. frutescens inhibited NO production in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells through simultaneous induction of HO-1 and inhibition of MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways.
Keywords: MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways; Perilla frutescens; anti-inflammation; heme oxygenase-1; rosmarinic acid methyl ester.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hispolon Suppresses LPS- or LTA-Induced iNOS/NO Production and Apoptosis in BV-2 Microglial Cells.Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(8):1649-1666. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500896. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Am J Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 29121802
-
7-Methoxy-(9H-β-Carbolin-1-il)-(E)-1-Propenoic Acid, a β-Carboline Alkaloid From Eurycoma longifolia, Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Activating the Nrf2/Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Mar;117(3):659-70. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25315. Epub 2015 Sep 3. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26291957
-
Downregulation of NO and PGE2 in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells by trans-isoferulic acid via suppression of PI3K/Akt-dependent NF-κB and activation of Nrf2-mediated HO-1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Jan;18(1):203-11. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.11.020. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24291391
-
4,7-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-1,3-benzodioxole from Antrodia camphorata inhibits LPS-induced inflammation via suppression of NF-κB and induction HO-1 in RAW264.7 cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Feb;31:186-94. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.12.030. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26745712
-
A new steroidal saponin, furotrilliumoside from Trillium tschonoskii inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in Raw264.7 cells by targeting PI3K/Akt, MARK and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.Fitoterapia. 2016 Dec;115:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Fitoterapia. 2016. PMID: 27693742
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial and Antitumor Photodynamic Effects of Phleichrome from the Phytopathogenic Fungus Cladosporium Phlei.Mycobiology. 2018 Dec 21;46(4):448-451. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2018.1551599. eCollection 2018. Mycobiology. 2018. PMID: 30637154 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Biological Role of α-Mangostin via TAK1-NF-κB Pathway against Inflammatory.Inflammation. 2019 Feb;42(1):103-112. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0876-6. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30132203
-
Identification of a novel S6K1 inhibitor, rosmarinic acid methyl ester, for treating cisplatin-resistant cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 6;19(1):773. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5997-2. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31387554 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products and Inflammation.Molecules. 2017 Jan 12;22(1):120. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010120. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28085099 Free PMC article.
-
Nepetoidin B from Salvia plebeia R. Br. Inhibits Inflammation by Modulating the NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Macrophage Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 28;10(8):1208. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081208. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim K.N., Heo S.J., Yoon W.J., Kang S.M., Ahn G., Yi T.H., Jeon Y.J. Fucoxanthin inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010;649:369–375. - PubMed
-
- Guzik T.J., Korbut R., Adamek-Guzik T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003;54:469–487. - PubMed
-
- Nathan C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature. 2002;420:846–852. - PubMed
-
- Walsh N.C., Crotti T.N., Goldring S.R., Gravallese E.M. Rheumatic diseases: The effects of inflammation on bone. Immunol. Rev. 2005;208:228–251. - PubMed
-
- Lee H.J., Hyun E.A., Yoon W.J., Kim B.H., Rhee M.H., Kang H.K., Cho J.Y., Yoo E.S. In vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of Cinnamomum camphora extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006;103:208–216. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

