Theophylline-Based KMUP-1 Improves Steatohepatitis via MMP-9/IL-10 and Lipolysis via HSL/p-HSL in Obese Mice
- PMID: 27548140
- PMCID: PMC5000741
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17081345
Theophylline-Based KMUP-1 Improves Steatohepatitis via MMP-9/IL-10 and Lipolysis via HSL/p-HSL in Obese Mice
Abstract
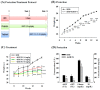
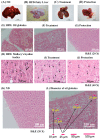
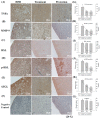
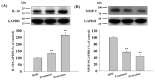
KMUP-1 (7-[2-[4-(2-chlorobenzene)piperazinyl]ethyl]-1,3-dimethylxanthine) has been reported to cause hepatic fat loss. However, the action mechanisms of KMUP-1 in obesity-induced steatohepatitis remains unclear. This study elucidated the steatohepatitis via matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), and related lipolysis via hormone sensitive lipase (HSL) and adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) by KMUP-1. KMUP-1 on steatohepatitis-associated HSL/p-HSL/ATGL/MMP-9/TNFα/interleukin-10 (IL-10) and infiltration of M1/M2 macrophages in obese mice were examined. KMUP-1 was administered by oral gavage from weeks 1-14 in high-fat diet (HFD)-supplemented C57BL/6J male mice (protection group) and from weeks 8-14, for 6 weeks, in HFD-induced obese mice (treatment group). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of tissues, oil globules number and size, infiltration and switching of M1/M2 macrophages were measured to determine the effects on livers. IL-10 and MMP-9 proteins were explored to determine the effects of KMUP-1 on M1/M2 macrophage polarization in HFD-induced steatohepatitis. Long-term administration of KMUP-1 reversed HFD-fed mice increased in body weight, sGOT/sGPT, triglyceride (TG) and glucose. Additionally, KMUP-1 decreased MMP-9 and reactive oxygen species (ROS), and increased HSL/p-HSL and IL-10 in HFD mice livers. In conclusion, KMUP-1, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor (PDEI), was shown to reduce lipid accumulation in liver tissues, suggesting that it could be able to prevent or treat steatohepatitis induced by HFD.
Keywords: M1/M2 macrophage; adipose triglyceride lipase; fatty liver; hormone sensitive lipase; matrix metallopeptidase 9; tumor necrosis factor α.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Xanthine-based KMUP-1 improves HDL via PPARγ/SR-B1, LDL via LDLRs, and HSL via PKA/PKG for hepatic fat loss.J Lipid Res. 2015 Nov;56(11):2070-84. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M057547. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26351364 Free PMC article.
-
KMUP-1, a GPCR Modulator, Attenuates Triglyceride Accumulation Involved MAPKs/Akt/PPARγ and PKA/PKG/HSL Signaling in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes.Molecules. 2018 Sep 23;23(10):2433. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102433. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30249030 Free PMC article.
-
Fat-reducing effects of dehydroepiandrosterone involve upregulation of ATGL and HSL expression, and stimulation of lipolysis in adipose tissue.Steroids. 2012 Nov;77(13):1359-65. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Steroids. 2012. PMID: 22951290
-
Exercise training inhibits inflammation in adipose tissue via both suppression of macrophage infiltration and acceleration of phenotypic switching from M1 to M2 macrophages in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice.Exerc Immunol Rev. 2010;16:105-18. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20839495
-
Effects of puerarin on lipid accumulation and metabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 30;10(3):e0122925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122925. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25822741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sesamol Alleviates Obesity-Related Hepatic Steatosis via Activating Hepatic PKA Pathway.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 26;12(2):329. doi: 10.3390/nu12020329. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31991934 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative proteomics and metabolomics of Guizhou Miao Sour Soup affecting simple obese rats.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 3;9:1019205. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1019205. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36407552 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamol intervention ameliorates obesity-associated metabolic disorders by regulating hepatic lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.Food Nutr Res. 2019 Oct 23;63. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v63.3637. eCollection 2019. Food Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 31692782 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Hypolipidemic Effects and Mechanisms of Phytochemicals: A Review.Foods. 2022 Sep 9;11(18):2774. doi: 10.3390/foods11182774. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36140902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do We Build Similar Molecules for Comorbid Diseases? Tevarud in Drug Design, an Analysis for Depression and Inflammation.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Jan 16;11(2):147-153. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00519. eCollection 2020 Feb 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32071681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu C.P., Dai Z.K., Huang C.H., Yeh J.L., Wu B.N., Wu J.R., Chen I.J. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase-enhancing G-protein coupled receptor antagonist inhibits pulmonary artery hypertension by endothelin-1-dependent and endothelin-1-independent pathways in a monocrotaline model. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2014;30:267–278. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2014.02.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dai Z.K., Lin T.C., Liou J.C., Cheng K.I., Chen J.Y., Chu L.W., Chen I.J., Wu B.N. Xanthine derivative KMUP-1 reduces inflammation and hyperalgesia in a bilateral chronic constriction injury model by suppressing MAPK and NFκB activation. Mol. Pharm. 2014;11:1621–1631. doi: 10.1021/mp5000086. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liou S.F., Hsu J.H., Chen Y.T., Chen I.J., Yeh J.L. KMUP-1 attenuates endothelin-1-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through activation of heme oxygenase-1 and suppression of the Akt/GSK-3β, calcineurin/NFATc4 and RhoA/ROCK pathways. Molecules. 2015;20:10435–10449. doi: 10.3390/molecules200610435. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chung H.H., Dai Z.K., Wu B.N., Yeh J.L., Chai C.Y., Chu K.S., Liu C.P., Chen I.J. KMUP-1 inhibits pulmonary artery proliferation by targeting serotonin receptors/transporter and NO synthase, inactivating RhoA and suppressing AKT/ERK phosphorylation. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2010;53:239–249. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2010.09.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

