Secondary Metabolites in Ramalina terebrata Detected by UHPLC/ESI/MS/MS and Identification of Parietin as Tau Protein Inhibitor
- PMID: 27548142
- PMCID: PMC5000700
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17081303
Secondary Metabolites in Ramalina terebrata Detected by UHPLC/ESI/MS/MS and Identification of Parietin as Tau Protein Inhibitor
Abstract
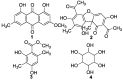
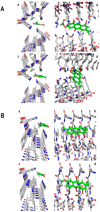
Liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry is an outstanding methodology for fast analysis of phenolic compounds in biological samples. Twenty two compounds were quickly and accurately identified in the methanolic extract of the Antarctic lichen Ramalina terebrata for the first time using ultra high pressure liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detector and high resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-PDA-Q/Orbitrap/MS/MS). In addition, the extract and the four compounds isolated from this species were tested for the inhibitory activity of tau protein aggregation, which is a protein involved in Alzheimer's disease (AD). All compounds showed null activity with the exception of parietin, which it was able to inhibit aggregation process of tau in a concentration range between 3 µg/mL (10 µM) to 28 µg/mL (100 µM). In addition, we show how parietin interact with tau (306)VQIVYK(311) hexapeptide inside of the microtubule binding domain (4R) with the help of molecular docking experiments. Finally, the constituents present in the methanolic extract could possibly contribute to the established anti-aggregation activity for this extract and this in-depth analysis of the chemical composition of R. terebrata could guide further research into its medicinal properties and potential uses.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Ramalina; UHPLC/MS; docking; lichens; parietin; tau protein.
Figures
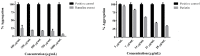
Similar articles
-
UHPLC-HRMS/MS Based Profiling of Algerian Lichens and Their Antimicrobial Activities.Chem Biodivers. 2018 Apr;15(4):e1800031. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201800031. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Chem Biodivers. 2018. PMID: 29505125
-
Lichen secondary metabolites from the cultured lichen mycobionts of Teloschistes chrysophthalmus and Ramalina celastri and their antiviral activities.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2007 Jul-Aug;62(7-8):543-9. doi: 10.1515/znc-2007-7-813. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17913069
-
Secondary Metabolite Profiling of Species of the Genus Usnea by UHPLC-ESI-OT-MS-MS.Molecules. 2017 Dec 27;23(1):54. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010054. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29280946 Free PMC article.
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
-
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination and profiling of prohibited steroids in human biological matrices. A review.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 May 15;927:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23317577 Review.
Cited by
-
Chrysophanol, Physcion, Hesperidin and Curcumin Modulate the Gene Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators Induced by LPS in HepG2: In Silico and Molecular Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Sep 3;8(9):371. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090371. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31484451 Free PMC article.
-
Are Ionic Liquids Better Extracting Agents Than Toxic Volatile Organic Solvents? A Combination of Ionic Liquids, Microwave and LC/MS/MS, Applied to the Lichen Stereocaulon glareosum.Front Chem. 2020 May 29;8:450. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00450. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32548092 Free PMC article.
-
High Resolution UHPLC-MS Metabolomics and Sedative-Anxiolytic Effects of Latua pubiflora: A Mystic Plant used by Mapuche Amerindians.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jul 26;8:494. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00494. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28798689 Free PMC article.
-
UHPLC-Q/Orbitrap/MS/MS Fingerprinting, Free Radical Scavenging, and Antimicrobial Activity of Tessaria absinthiodes (Hook. & Arn.) DC. (Asteraceae) Lyophilized Decoction from Argentina and Chile.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Nov 28;8(12):593. doi: 10.3390/antiox8120593. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31795145 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant, Gastroprotective, Cytotoxic Activities and UHPLC PDA-Q Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry Identification of Metabolites in Baccharis grisebachii Decoction.Molecules. 2019 Mar 19;24(6):1085. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061085. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30893865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shukla V., Joshi G., Rawat M.S.M. Lichens as a potential natural source of bioactive compounds: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2010;9:303–314. doi: 10.1007/s11101-010-9189-6. - DOI
-
- Basile A., Rigano D., Loppi S., di Santi A., Nebbioso A., Sorbo S., Conte B., Paoli L., de Ruberto F., Molinari A.M., et al. Antiproliferative, antibacterial and antifungal activity of the lichen Xanthoria parietina and its secondary metabolite parietin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015;16:7861–7875. doi: 10.3390/ijms16047861. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boustie J., Grube M. Lichens—A promising source of bioactive secondary metabolites. Plant Genet. Resour. 2005;3:273–287. doi: 10.1079/PGR200572. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

