KdmB, a Jumonji Histone H3 Demethylase, Regulates Genome-Wide H3K4 Trimethylation and Is Required for Normal Induction of Secondary Metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 27548260
- PMCID: PMC4993369
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006222
KdmB, a Jumonji Histone H3 Demethylase, Regulates Genome-Wide H3K4 Trimethylation and Is Required for Normal Induction of Secondary Metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
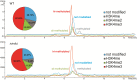
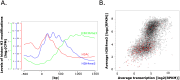
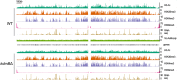
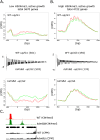
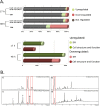
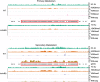
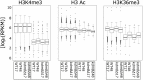
Histone posttranslational modifications (HPTMs) are involved in chromatin-based regulation of fungal secondary metabolite biosynthesis (SMB) in which the corresponding genes-usually physically linked in co-regulated clusters-are silenced under optimal physiological conditions (nutrient-rich) but are activated when nutrients are limiting. The exact molecular mechanisms by which HPTMs influence silencing and activation, however, are still to be better understood. Here we show by a combined approach of quantitative mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP-seq) and transcriptional network analysis (RNA-seq) that the core regions of silent A. nidulans SM clusters generally carry low levels of all tested chromatin modifications and that heterochromatic marks flank most of these SM clusters. During secondary metabolism, histone marks typically associated with transcriptional activity such as H3 trimethylated at lysine-4 (H3K4me3) are established in some, but not all gene clusters even upon full activation. KdmB, a Jarid1-family histone H3 lysine demethylase predicted to comprise a BRIGHT domain, a zinc-finger and two PHD domains in addition to the catalytic Jumonji domain, targets and demethylates H3K4me3 in vivo and mediates transcriptional downregulation. Deletion of kdmB leads to increased transcription of about ~1750 genes across nutrient-rich (primary metabolism) and nutrient-limiting (secondary metabolism) conditions. Unexpectedly, an equally high number of genes exhibited reduced expression in the kdmB deletion strain and notably, this group was significantly enriched for genes with known or predicted functions in secondary metabolite biosynthesis. Taken together, this study extends our general knowledge about multi-domain KDM5 histone demethylases and provides new details on the chromatin-level regulation of fungal secondary metabolite production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128(4):693–705. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

