Rho GTPases, their post-translational modifications, disease-associated mutations and pharmacological inhibitors
- PMID: 27548350
- PMCID: PMC5927519
- DOI: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1218407
Rho GTPases, their post-translational modifications, disease-associated mutations and pharmacological inhibitors
Abstract
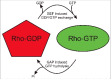
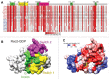
The 20 members of the Rho GTPase family are key regulators of a wide-variety of biological activities. In response to activation, they signal via downstream effector proteins to induce dynamic alterations in the organization of the actomyosin cytoskeleton. In this review, post-translational modifications, mechanisms of dysregulation identified in human pathological conditions, and the ways that Rho GTPases might be targeted for chemotherapy will be discussed.
Keywords: CDC42; GTPase; Rac; Rho; actin; mutation; phosphorylation; signal transduction; ubiquitin.
Figures
References
-
- Madaule P, Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell 1985; 41:31-40; PMID:3888408; https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paterson HF, Self AJ, Garrett MD, Just I, Aktories K, Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol 1990; 111:1001-7; PMID:2118140; https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell 1992; 70:389-99; PMID:1643657; https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL, Diekmann D, Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 1992; 70:401-10; PMID:1643658; https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
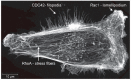
- Nobes CD, Hall A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 1995; 81:53-62; PMID:7536630; https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
