Tumors Alter Inflammation and Impair Dermal Wound Healing in Female Mice
- PMID: 27548621
- PMCID: PMC4993492
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161537
Tumors Alter Inflammation and Impair Dermal Wound Healing in Female Mice
Abstract
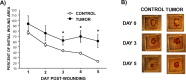
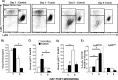
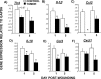
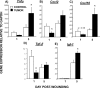
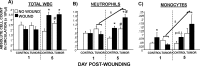
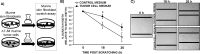
Tissue repair is an integral component of cancer treatment (e.g., due to surgery, chemotherapy, radiation). Previous work has emphasized the immunosuppressive effects of tumors on adaptive immunity and has shown that surgery incites cancer metastases. However, the extent to which and how tumors may alter the clinically-relevant innate immune process of wound healing remains an untapped potential area of improvement for treatment, quality of life, and ultimately, mortality of cancer patients. In this study, 3.5 mm full-thickness dermal excisional wounds were placed on the dorsum of immunocompetent female mice with and without non-malignant flank AT-84 murine oral squamous cell carcinomas. Wound closure rate, inflammatory cell number and inflammatory signaling in wounds, and circulating myeloid cell concentrations were compared between tumor-bearing and tumor-free mice. Tumors delayed wound closure, suppressed inflammatory signaling, and altered myeloid cell trafficking in wounds. An in vitro scratch "wounding" assay of adult dermal fibroblasts treated with tumor cell-conditioned media supported the in vivo findings. This study demonstrates that tumors are sufficient to disrupt fundamental and clinically-relevant innate immune functions. The understanding of these underlying mechanisms provides potential for therapeutic interventions capable of improving the treatment of cancer while reducing morbidities and mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- de Araujo T, Valencia I, Federman DG, Kirsner RS. Managing the patient with venous ulcers. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(4):326–34. Epub 2003/02/15. . - PubMed
-
- McNees P, Meneses KD. Pressure ulcers and other chronic wounds in patients with and patients without cancer: a retrospective, comparative analysis of healing patterns. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2007;53(2):70–8. Epub 2007/02/13. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

