Health effects of 'Juntos', a conditional cash transfer programme in Peru
- PMID: 27549365
- PMCID: PMC6866111
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12348
Health effects of 'Juntos', a conditional cash transfer programme in Peru
Abstract
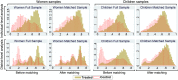
In some countries, conditional cash transfer (CCT) programmes show an impact on maternal and child health. Juntos, the CCT programme in Peru, has been evaluated several times operationally, but seldom for maternal and child health outcomes. The objective of this study is to evaluate the impact of Juntos on children under 6 years, pregnant women and mothers of children under 17 years. Outcomes evaluated included (1) anaemia in women and children; (2) acute malnutrition in children; (3) post-partum complications in mothers; and (4) underweight and overweight in mothers. We identified Juntos eligible respondents from the Demographic and Health Surveys of Peru for years 2007 to 2013. Propensity score matching was used to identify comparable treatment and control groups, including eligible respondents enrolled in Juntos vs. those not enrolled in Juntos (individual-level analysis), as well as eligible respondents living in Juntos districts vs. those not residing in Juntos districts (district-level analysis). We then used generalized linear models to estimate prevalence ratios. Individual level analysis showed that Juntos reduced underweight in women (PR:0.39, 95%CI:0.18 - 0.85) and anaemia in children (PR:0.93, 95%CI:0.86 - 1.00). In the district level analysis, the programme was associated with a reduction of overweight in women (PR:0.94, 95%CI:0.90 - 0.98) and acute malnutrition in children (PR:0.49, 95%CI:0.32 - 0.73), but an increase in the prevalence of anaemia in children (PR:1.09, 95%CI:1.01 - 1.17). We found that Juntos had an effect on maternal and child health indicators, but further studies are required to overcome some limitations encountered here.
Keywords: Health Policy; anaemia; child care; conditional cash transfer programmes; malnutrition; nutritional status; propensity score matching.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alcázar L. (2009) El gasto público social frente a la infancia: Análisis del programa Juntos y de la oferta y demanda de servicios asociadas a sus condiciones. Grade—Niños Milen.
-
- Álvarez‐Dongo D., Sánchez‐Abanto J., Gómez‐Guizado G. & Tarqui‐Mamani C. (2012) Sobrepeso y obesidad: prevalencia y determinantes sociales del exceso de peso en la población peruana (2009–2010). Revista Peruana de Medicina Experimental y Salud Pública 29, 303–313. - PubMed
-
- Andersen C.T., Reynolds S.A., Behrman J.R., Crookston B.T., Dearden K.A., Escobal J. et al. (2015) Participation in the Juntos conditional cash transfer program in Peru is associated with changes in child anthropometric status but not language development or school achievement. Journal of Nutrition jn213546.. DOI: 10.3945/jn.115.213546. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aramburú C.E. (2010) Informe compilatorio: El Programa Juntos, resultados y retos.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

