Glutamatergic and Neuronal Dysfunction in Gray and White Matter: A Spectroscopic Imaging Study in a Large Schizophrenia Sample
- PMID: 27550776
- PMCID: PMC5473520
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbw122
Glutamatergic and Neuronal Dysfunction in Gray and White Matter: A Spectroscopic Imaging Study in a Large Schizophrenia Sample
Abstract
Glutamine plus glutamate (Glx), as well as N-acetylaspartate compounds (NAAc, N-acetylaspartate plus N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate), a marker of neuronal viability, can be quantified with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). We used 1H-MRS imaging to assess Glx and NAAc, as well as total-choline (glycerophospho-choline plus phospho-choline), myo-inositol and total-creatine (creatine plus phosphocreatine) from an axial supraventricular slab of gray matter (GM, medial-frontal and medial-parietal) and white matter (WM, bilateral-frontal and bilateral-parietal) voxels. Schizophrenia subjects (N = 104) and healthy controls (N = 97) with a broad age range (16 to 65) were studied. In schizophrenia, Glx was increased in GM (P < .001) and WM (P = .01), regardless of age. However, with greater age, NAAc increased in GM (P < .001) but decreased in WM (P < .001) in schizophrenia. In patients, total creatine decreased with age in WM (P < .001). Finally, overall cognitive score correlated positively with WM neurometabolites in controls but negatively in the schizophrenia group (NAAc, P < .001; and creatine [only younger], P < .001). We speculate the results support an ongoing process of increased glutamate metabolism in schizophrenia. Later in the illness, disease progression is suggested by increased cortical compaction without neuronal loss (elevated NAAc) and reduced axonal integrity (lower NAAc). Furthermore, this process is associated with fundamentally altered relationships between neurometabolite concentrations and cognitive function in schizophrenia.
Keywords: 1H-MRS; N-acetylaspartate; creatine; glutamate; schizophrenia; total-choline.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
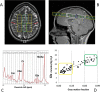
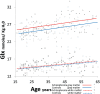


References
-
- Green MF, Kern RS, Braff DL, Mintz J. Neurocognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia: are we measuring the “right stuff”? Schizophr Bull. 2000;26:119–136. - PubMed
-
- Olney JW, Farber NB. Glutamate receptor dysfunction and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52:998–1007. - PubMed
-
- Steen RG, Hamer RM, Lieberman JA. Measurement of brain metabolites by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:1949–1962. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

