Precision glycocalyx editing as a strategy for cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 27551071
- PMCID: PMC5027407
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1608069113
Precision glycocalyx editing as a strategy for cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
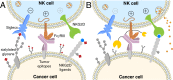
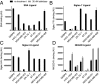
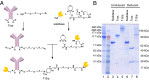
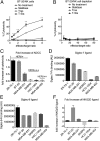
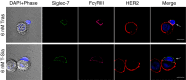
Cell surface sialosides constitute a central axis of immune modulation that is exploited by tumors to evade both innate and adaptive immune destruction. Therapeutic strategies that target tumor-associated sialosides may therefore potentiate antitumor immunity. Here, we report the development of antibody-sialidase conjugates that enhance tumor cell susceptibility to antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) by selective desialylation of the tumor cell glycocalyx. We chemically fused a recombinant sialidase to the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-specific antibody trastuzumab through a C-terminal aldehyde tag. The antibody-sialidase conjugate desialylated tumor cells in a HER2-dependent manner, reduced binding by natural killer (NK) cell inhibitory sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec) receptors, and enhanced binding to the NK-activating receptor natural killer group 2D (NKG2D). Sialidase conjugation to trastuzumab enhanced ADCC against tumor cells expressing moderate levels of HER2, suggesting a therapeutic strategy for cancer patients with lower HER2 levels or inherent trastuzumab resistance. Precision glycocalyx editing with antibody-enzyme conjugates is therefore a promising avenue for cancer immune therapy.
Keywords: ADCC; Siglec; cancer immune therapy; sialic acid; trastuzumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cutting back on the carbs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 13;113(37):10228-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612432113. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27588908 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

