Organization of some repetitive DNAs and B chromosomes in the grasshopper Eumastusia koebelei koebelei (Rehn, 1909) (Orthoptera, Acrididae, Leptysminae)
- PMID: 27551344
- PMCID: PMC4977798
- DOI: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i2.7609
Organization of some repetitive DNAs and B chromosomes in the grasshopper Eumastusia koebelei koebelei (Rehn, 1909) (Orthoptera, Acrididae, Leptysminae)
Abstract
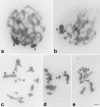
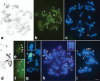
B chromosomes occur in approximately 15% of eukaryotes and are usually heterochromatic and rich in repetitive DNAs. Here we describe characteristics of a B chromosome in the grasshopper Eumastusia koebelei koebelei (Rehn, 1909) through classical cytogenetic methods and mapping of some repetitive DNAs, including multigene families, telomeric repeats and a DNA fraction enriched with repetitive DNAs obtained from DOP-PCR. Eumastusia koebelei koebelei presented 2n=23, X0 and, in one individual, two copies of the same variant of a B chromosome were noticed, which are associated during meiosis. The C-positive blocks were located in the pericentromeric regions of the standard complement and along the entire length of the B chromosomes. Some G+C-rich heterochromatic blocks were noticed, including conspicuous blocks in the B chromosomes. The mapping of 18S rDNA and U2 snDNA revealed only autosomal clusters, and the telomeric probe hybridized in terminal regions. Finally, the DOP-PCR probe obtained from an individual without a B chromosome revealed signals in the heterochromatic regions, including the entire length of the B chromosome. The possible intraspecific origin of the B chromosomes, due to the shared pool of repetitive DNAs between the A and B chromosomes and the possible consequences of their association are discussed.
Keywords: Cytogenetics; DOP-PCR; FISH; Orthoptera; multigene family.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromosomal Mapping of Repetitive DNAs in the Grasshopper Abracris flavolineata Reveal Possible Ancestry of the B Chromosome and H3 Histone Spreading.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e66532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066532. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826099 Free PMC article.
-
High similarity of U2 snDNA sequence between A and B chromosomes in the grasshopper Abracris flavolineata.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Oct;290(5):1787-92. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1033-7. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25846962
-
Contrasting the Chromosomal Organization of Repetitive DNAs in Two Gryllidae Crickets with Highly Divergent Karyotypes.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 2;10(12):e0143540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143540. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26630487 Free PMC article.
-
Microsatellite organization in the grasshopper Abracris flavolineata (Orthoptera: Acrididae) revealed by FISH mapping: remarkable spreading in the A and B chromosomes.PLoS One. 2014 May 28;9(5):e97956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097956. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24871300 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive DNA chromosomal organization in the cricket Cycloptiloides americanus: a case of the unusual X1X 20 sex chromosome system in Orthoptera.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Apr;290(2):623-31. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0947-9. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25373534
Cited by
-
Karyotypic description of the stingless bee Meliponaquinquefasciata Lepeletier, 1836 (Hymenoptera, Meliponini) with emphasis on the presence of B chromosomes.Comp Cytogenet. 2018 Nov 9;12(4):471-482. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v12i4.29165. eCollection 2018. Comp Cytogenet. 2018. PMID: 30479700 Free PMC article.
-
The satellite DNA AflaSAT-1 in the A and B chromosomes of the grasshopper Abracris flavolineata.BMC Genet. 2017 Aug 29;18(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12863-017-0548-9. BMC Genet. 2017. PMID: 28851268 Free PMC article.
-
Wide dispersion of B chromosomes in Rhammatocerus brasiliensis (Orthoptera, Acrididae).Genet Mol Biol. 2020 Jun 10;43(3):e20190077. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0077. eCollection 2020. Genet Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32542305 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehending the dynamism of B chromosomes in their journey towards becoming unselfish.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 4;10:1072716. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1072716. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36684438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amedegnato C. (1974) Les genres d’acridiens néotropicaux, leur classification par familles, sous-familles et tribus. Acrida 3: 193–204.
-
- Anjos A, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Camacho JPM, Loreto V, Cabrero J, Souza MJ, Cabral-de-Mello DC. (2015) U1 snDNA clusters in grasshoppers: chromosomal dynamics and genomic organization. Heredity 114: 207–219. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2014.87 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banaei-Moghaddam AM, Martis MM, Macas J, Gundlach H, Himmelbach A, Altschmied L, Mayer KF, Houben A. (2015) Genes on B chromosomes: old questions revisited with new tools. Biochimica Biophysica Acta 1849: 64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.11.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bidau CJ, Hasson ER. (1984) Population cytology of Leptysma argentina Bruner (Leptysminae, Acrididae). Genetica 62: 161–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00056433 - DOI
-
- Bueno D, Palacios-Gimenez OM, Cabral-de-Mello DC. (2013) Chromosomal Mapping of Repetitive DNAs in the Grasshopper Abracris flavolineata Reveal Possible Ancestry of the B Chromosome and H3 Histone Spreading. PLoS ONE 8: . doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066532 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
