WWOX dysfunction induces sequential aggregation of TRAPPC6AΔ, TIAF1, tau and amyloid β, and causes apoptosis
- PMID: 27551439
- PMCID: PMC4981022
- DOI: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.3
WWOX dysfunction induces sequential aggregation of TRAPPC6AΔ, TIAF1, tau and amyloid β, and causes apoptosis
Abstract
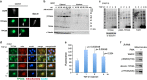
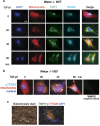
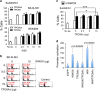
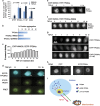
Aggregated vesicle-trafficking protein isoform TRAPPC6AΔ (TPC6AΔ) has a critical role in causing caspase activation, tau aggregation and Aβ generation in the brains of nondemented middle-aged humans, patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and 3-week-old Wwox gene knockout mice. WWOX blocks neurodegeneration via interactions with tau and tau-phosphorylating enzymes. WWOX deficiency leads to epilepsy, mental retardation and early death. Here, we demonstrated that TGF-β1 induces shuttling of endogenous wild-type TPC6A and TPC6AΔ in between nucleoli and mitochondria (~40-60 min per round trip), and WWOX reduces the shuttling time by 50%. TGF-β1 initially maximizes the binding of TPC6AΔ to the C-terminal tail of WWOX, followed by dissociation. TPC6AΔ then undergoes aggregation, together with TIAF1 (TGF-β1-induced antiapoptotic factor), in the mitochondria to induce apoptosis. An additional rescue scenario is that TGF-β1 induces Tyr33 phosphorylation and unfolding of WWOX and its the N-terminal WW domain slowly binds TPC6AΔ to block aggregation and apoptosis. Similarly, loss of WWOX induces TPC6AΔ polymerization first, then aggregation of TIAF1, amyloid β and tau, and subsequent cell death, suggesting that a cascade of protein aggregation leads to neurodegeneration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A p53/TIAF1/WWOX triad exerts cancer suppression but may cause brain protein aggregation due to p53/WWOX functional antagonism.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Jul 17;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0382-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31315632 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking protein particle complex 6A delta (TRAPPC6AΔ) is an extracellular plaque-forming protein in the brain.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):3578-89. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2876. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25650666 Free PMC article.
-
Zfra Inhibits the TRAPPC6AΔ-Initiated Pathway of Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 22;23(23):14510. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314510. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498839 Free PMC article.
-
WWOX Phosphorylation, Signaling, and Role in Neurodegeneration.Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 15;12:563. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00563. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30158849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zfra Overrides WWOX in Suppressing the Progression of Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 20;25(6):3507. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063507. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
WWOX Controls Cell Survival, Immune Response and Disease Progression by pY33 to pS14 Transition to Alternate Signaling Partners.Cells. 2022 Jul 7;11(14):2137. doi: 10.3390/cells11142137. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chasing the signaling run by tri-molecular time-lapse FRET microscopy.Cell Death Discov. 2018 Mar 22;4:45. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0047-4. eCollection 2018. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 29581896 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Structure and Function of TRAPP Complexes in the Cardiac System.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023 Jul 12;8(12):1599-1612. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.03.011. eCollection 2023 Dec. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38205348 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of expression signatures of neuronal subpopulations in the VTA.Mol Brain. 2019 Dec 11;12(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0530-8. Mol Brain. 2019. PMID: 31829254 Free PMC article.
-
A p53/TIAF1/WWOX triad exerts cancer suppression but may cause brain protein aggregation due to p53/WWOX functional antagonism.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Jul 17;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0382-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31315632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gwynn B, Smith RS, Rowe LB, Taylor BA, Peters LL. A mouse TRAPP-related protein is involved in pigmentation. Genomics 2006; 88: 196–203. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

