Characterization of GSK'963: a structurally distinct, potent and selective inhibitor of RIP1 kinase
- PMID: 27551444
- PMCID: PMC4979471
- DOI: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.9
Characterization of GSK'963: a structurally distinct, potent and selective inhibitor of RIP1 kinase
Abstract
Necroptosis and signaling regulated by RIP1 kinase activity is emerging as a key driver of inflammation in a variety of disease settings. A significant amount has been learned about how RIP1 regulates necrotic cell death through the use of the RIP1 kinase inhibitor Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1). Nec-1 has been a transformational tool for exploring the function of RIP1 kinase activity; however, its utility is somewhat limited by moderate potency, off-target activity against indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), and poor pharmacokinetic properties. These limitations of Nec-1 have driven an effort to identify next-generation tools to study RIP1 function, and have led to the identification of 7-Cl-O-Nec-1 (Nec-1s), which has improved pharmacokinetic properties and lacks IDO inhibitory activity. Here we describe the characterization of GSK'963, a chiral small-molecule inhibitor of RIP1 kinase that is chemically distinct from both Nec-1 and Nec-1s. GSK'963 is significantly more potent than Nec-1 in both biochemical and cellular assays, inhibiting RIP1-dependent cell death with an IC50 of between 1 and 4 nM in human and murine cells. GSK'963 is >10 000-fold selective for RIP1 over 339 other kinases, lacks measurable activity against IDO and has an inactive enantiomer, GSK'962, which can be used to confirm on-target effects. The increased in vitro potency of GSK'963 also translates in vivo, where GSK'963 provides much greater protection from hypothermia at matched doses to Nec-1, in a model of TNF-induced sterile shock. Together, we believe GSK'963 represents a next-generation tool for examining the function of RIP1 in vitro and in vivo, and should help to clarify our current understanding of the role of RIP1 in contributing to disease pathogenesis.
Figures
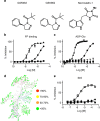
 =Nec-1,
=Nec-1,  =GSK′962,
=GSK′962,  =GSK′963 and
=GSK′963 and  =Menadione.
=Menadione.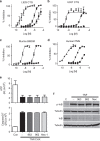
 =Nec-1,
=Nec-1,  =GSK′962, and
=GSK′962, and  =GSK′963. C, control; CHX, cycloheximide.
=GSK′963. C, control; CHX, cycloheximide.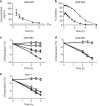
 =2 mg/kg and
=2 mg/kg and  =0.2 mg/kg (c–e) The effect of GSK′963, GSK′962 and Nec-1 on temperature loss in the TNF+zVAD-induced shock model. C57BL/6 mice were pretreated i.p. with (c) GSK′963, (d) GSK′962A or (e) Nec-1 15 min prior to i.v. injection of TNF+zVAD. Temperature was monitored over the course of 3 h by rectal probe. The results are representative of three independent experiments, each containing seven animals per group. Error bars indicate the S.D. from the seven animals for each group.
=0.2 mg/kg (c–e) The effect of GSK′963, GSK′962 and Nec-1 on temperature loss in the TNF+zVAD-induced shock model. C57BL/6 mice were pretreated i.p. with (c) GSK′963, (d) GSK′962A or (e) Nec-1 15 min prior to i.v. injection of TNF+zVAD. Temperature was monitored over the course of 3 h by rectal probe. The results are representative of three independent experiments, each containing seven animals per group. Error bars indicate the S.D. from the seven animals for each group.  =control mice,
=control mice,  =TNF+zVAD-treated mice,
=TNF+zVAD-treated mice,  =TNF+zVAD-treated mice dosed with GSK′963 at 0.2 mg/kg,
=TNF+zVAD-treated mice dosed with GSK′963 at 0.2 mg/kg,  =TNF+zVAD-treated mice dosed with GSK′963 at 2 mg/kg,
=TNF+zVAD-treated mice dosed with GSK′963 at 2 mg/kg,  =TNF+zVAD-treated mice dosed with GSK′962 at 20 mg/kg,
=TNF+zVAD-treated mice dosed with GSK′962 at 20 mg/kg,  =TNF+zVAD with Nec-1 at 2 mg/kg and
=TNF+zVAD with Nec-1 at 2 mg/kg and  =TNF+zVAD with Nec-1 at 0.2 mg/kg.
=TNF+zVAD with Nec-1 at 0.2 mg/kg.References
-
- Meylan E , Burns K , Hofmann K , Blancheteau V , Martinon F , Kelliher M et al. RIP1 is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 3-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 503–507. - PubMed
-
- Cusson-Hermance N , Khurana S , Lee TH , Fitzgerald KA , Kelliher MA . Rip1 mediates the Trif-dependent toll-like receptor 3- and 4-induced NF-{kappa}B activation but does not contribute to interferon regulatory factor 3 activation. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 36560–36566. - PubMed
-
- Lee TH , Shank J , Cusson N , Kelliher MA . The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced IkappaB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 33185–33191. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

