ALS-associated mutant FUS inhibits macroautophagy which is restored by overexpression of Rab1
- PMID: 27551461
- PMCID: PMC4979432
- DOI: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.30
ALS-associated mutant FUS inhibits macroautophagy which is restored by overexpression of Rab1
Abstract
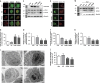
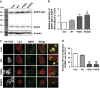
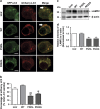
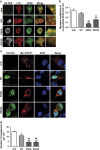
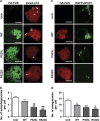
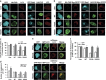
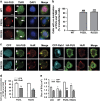
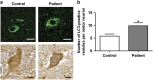
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is characterised by the formation of intracellular misfolded protein inclusions that form in motor neurons. Autophagy is the major degradation pathway for aggregate-prone proteins within lysosomes. Autophagy begins by the production of the omegasome, forming the autophagosome membrane, which then fuses with the lysosome. Mutations in fused in sarcoma (FUS) cause 5% of familial ALS cases and FUS-positive inclusions are also formed in sporadic ALS tissues. In this study, we demonstrate that the expression of ALS-associated mutant FUS impairs autophagy in neuronal cells. In mutant FUS-expressing neuronal cells, accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and autophagy substrates p62 and NBR1 was detected, and formation of both the omegasome and autophagosome was inhibited in these cells. However, overexpression of Rab1 rescued these defects, suggesting that Rab1 is protective in ALS. The number of LC3-positive vesicles was also increased in motor neurons from the spinal cord of an ALS patient carrying a FUS (R521C) mutation compared with a control patient, providing additional evidence that autophagy is dysregulated in mutant FUS-associated ALS. This study provides further understanding of the intricate autophagy system and neurodegeneration in ALS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rab1-dependent ER-Golgi transport dysfunction is a common pathogenic mechanism in SOD1, TDP-43 and FUS-associated ALS.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Nov;130(5):679-97. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1468-2. Epub 2015 Aug 23. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 26298469
-
Autophagy regulates amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked fused in sarcoma-positive stress granules in neurons.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Dec;35(12):2822-2831. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.07.026. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 25216585
-
Stepwise acquirement of hallmark neuropathology in FUS-ALS iPSC models depends on mutation type and neuronal aging.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Oct;82:420-429. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.07.017. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26253605
-
Role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Nov;1852(11):2517-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.08.005. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26264610 Review.
-
[Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) with the mutations in the fused in sarcoma/translocated in liposarcoma gene].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013;53(11):1080-3. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.53.1080. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2013. PMID: 24291885 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal dementia an autophagy disease?Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Dec 28;12(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0232-6. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 29282133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prionoid Proteins in the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 12;12:271. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00271. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31780895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathomechanistic Networks of Motor System Injury in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(11):1778-1806. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230824091601. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37622689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Immune Response as a Trigger of FUS Proteinopathy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 24;29(13):4496-4508.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.094. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31875556 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on the Small GTPase Rab1: A Key Player in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 8;22(21):12087. doi: 10.3390/ijms222112087. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kwiatkowski TJ , Bosco DA , Leclerc AL , Tamrazian E , Vanderburg CR , Russ C et al. Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2009; 323: 1205–1208. - PubMed
-
- Blair IP , Williams KL , Warraich ST , Durnall JC , Thoeng AD , Manavis J et al. FUS mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: clinical, pathological, neurophysiological and genetic analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2010; 81: 639–645. - PubMed
-
- Hewitt C , Kirby J , Highley JR , Hartley JA , Hibberd R , Hollinger HC et al. Novel FUS/TLS mutations and pathology in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 2010; 67: 455–461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

