Polyphenols act synergistically with doxorubicin and etoposide in leukaemia cell lines
- PMID: 27551472
- PMCID: PMC4979421
- DOI: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.43
Polyphenols act synergistically with doxorubicin and etoposide in leukaemia cell lines
Abstract
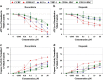
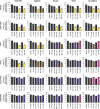
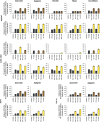
The study aimed to assess the effects of polyphenols when used in combination with doxorubicin and etoposide, and to determine whether polyphenols sensitised leukaemia cells, causing inhibition of cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis. This study is based on findings in solid cancer tumours, which have shown that polyphenols can sensitize cells to chemotherapy, and induce apoptosis and/or cell-cycle arrest. This could enable a reduction of chemotherapy dose and off-target effects, whilst maintaining treatment efficacy. Quercetin, apigenin, emodin, rhein and cis-stilbene were investigated alone and in combination with etoposide and doxorubicin in two lymphoid and two myeloid leukaemia cells lines. Measurements were made of ATP levels (using CellTiter-Glo assay) as an indication of total cell number, cell cycle progression (using propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry) and apoptosis (NucView caspase 3 assay and Hoechst 33342/propidium iodide staining). Effects of combination treatments on caspases 3, 8 and 9 activity were determined using Glo luminescent assays, glutathione levels were measured using the GSH-Glo Glutathione Assay and DNA damage determined by anti-γH2AX staining. Doxorubicin and etoposide in combination with polyphenols synergistically reduced ATP levels, induced apoptosis and increased S and/or G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in lymphoid leukaemia cell lines. However, in the myeloid cell lines the effects of the combination treatments varied; doxorubicin had a synergistic or additive effect when combined with quercetin, apigenin, emodin, and cis-stilbene, but had an antagonistic effect when combined with rhein. Combination treatment caused a synergistic downregulation of glutathione levels and increased DNA damage, driving apoptosis via caspase 8 and 9 activation. However, in myeloid cells where antagonistic effects were observed, this was associated with increased glutathione levels and a reduction in DNA damage and apoptosis. This study has demonstrated that doxorubicin and etoposide activity were enhanced by polyphenols in lymphoid leukaemia cells, however, differential responses were seen in myeloid cells with antagonistic responses seen in some combination therapies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular Action of Polyphenols in Leukaemia and Their Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3085. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063085. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols enhance the activity of alkylating agents in leukaemia cell lines.Oncotarget. 2019 Jul 16;10(44):4570-4586. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27068. eCollection 2019 Jul 16. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31360305 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of polyphenols on proliferation and apoptosis in human myeloid and lymphoid leukemia cell lines.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Dec;13(10):1601-13. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990303. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23796248 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary polyphenols influence antimetabolite agents: methotrexate, 6-mercaptopurine and 5-fluorouracil in leukemia cell lines.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 24;8(62):104877-104893. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20501. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285220 Free PMC article.
-
[Biological properties and sensitivity to induction therapy of differentiated cells expressing atypical immunophenotype in acute leukemia of children].Folia Med Cracov. 2001;42(3):5-80. Folia Med Cracov. 2001. PMID: 12353422 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Apigenin in cancer therapy: anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of action.Cell Biosci. 2017 Oct 5;7:50. doi: 10.1186/s13578-017-0179-x. eCollection 2017. Cell Biosci. 2017. PMID: 29034071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celastrol: A Review of Useful Strategies Overcoming its Limitation in Anticancer Application.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 18;11:558741. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.558741. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33364939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential of Phytochemicals in Oral Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Review of the Evidence.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 6;10(8):1150. doi: 10.3390/biom10081150. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32781654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Action of Polyphenols in Leukaemia and Their Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3085. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063085. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Olive Oil Mill Wastewater Extract Improves Chemotherapeutic Activity Against Breast Cancer Cells While Protecting From Cardiotoxicity.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 14;9:867867. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.867867. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35498037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leukaemia and lymphoma Research. Available at: https://leukaemialymphomaresearch.org.uk (accessed 08 June 2015).
-
- Cancer Research UK. Let's beat cancer sooner. Available at: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/ (accessed 08 June 2015).
-
- Mohan A , Narayanan S , Sethuraman S , Maheswari Krishnan U . Combinations of plant polyphenols & anti-cancer molecules: A novel treatment strategy for cancer chemotherapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2013; 13: 281–295. - PubMed
-
- Rossi S. Australian Medicines Handbook. The Australian Medicines Handbook Unit Trust: Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2013.
-
- Thakur DS . Topoisomerase II inhibitors in cancer treatment. Int J Pharm Nanotechnol 2011; 3: 1173–1181.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

