Tibial Plateau Fractures in Elderly Patients
- PMID: 27551570
- PMCID: PMC4976737
- DOI: 10.1177/2151458516651310
Tibial Plateau Fractures in Elderly Patients
Abstract
Tibial plateau fractures are common in the elderly population following a low-energy mechanism. Initial evaluation includes an assessment of the soft tissues and surrounding ligaments. Most fractures involve articular depression leading to joint incongruity. Treatment of these fractures may be complicated by osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and medical comorbidities. Optimal reconstruction should restore the mechanical axis, provide a stable construct for mobilization, and reestablish articular congruity. This is accomplished through a variety of internal or external fixation techniques or with acute arthroplasty. Regardless of the treatment modality, particular focus on preservation and maintenance of the soft tissue envelope is paramount.
Keywords: elderly; osteoporosis; tibial plateau fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
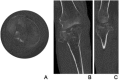

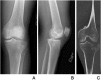
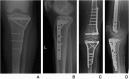

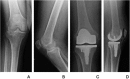
References
-
- Biyani A, Reddy NS, Chaudhury J, Simison AJ, Klenerman L. The results of surgical management of displaced tibial plateau fractures in the elderly. Injury. 1995;26(5):291–297. - PubMed
-
- Marsh JL. Tibial plateau fractures In: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults. 7th ed Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010:1780–1831.
-
- Langford JR, Jacofsky DJ, Haidukewych GJ. Tibial plateau fractures In: Scott WN, ed. Insall & Scott Surgery of the Knee. 5th ed Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2010:773–785.
-
- Abdel-Hamid MZ, Chang CH, Chan YS, et al. Arthroscopic evaluation of soft tissue injuries in tibial plateau fractures: retrospective analysis of 98 cases. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(6):669–675. - PubMed
-
- Hsu CJ, Chang WN, Wong CY. Surgical treatment of tibial plateau fracture in elderly patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001;121(1-2):67–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

