Medication Costs and Adherence of Treatment Before and After the Affordable Care Act: 1999-2015
- PMID: 27552279
- PMCID: PMC5024360
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2016.303269
Medication Costs and Adherence of Treatment Before and After the Affordable Care Act: 1999-2015
Abstract
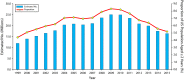
To examine national changes in rates of cost-related prescription nonadherence (CRN) by age group, we used data from the 1999-2015 Sample Adult and Sample Child National Health Interview Surveys (n = 768 781). In a logistic regression analysis of 2015 data, we identified subgroups at risk for cost-related nonadherence. The proportion of all Americans who did not fill a prescription in the previous 12 months because they could not afford it grew from 1999 to 2009, peaking at 8.3% at the height of the Great Recession and dropping to 5.2% by 2015. CRN among seniors, however, peaked in 2004 at 5.4% and dropped to 3.6% after implementation of Medicare Part D in 2006. CRN is responsive to improved access related to implementation of Medicare Part D and the Affordable Care Act.
Figures
References
-
- Thinking Outside the Pillbox: A System-Wide Approach to Improving Patient Medication Adherence for Chronic Disease. Cambridge, MA: New England Healthcare Institute; 2009.
-
- Kennedy J, Coyne J, Sclar D. Drug affordability and prescription noncompliance in the United States: 1997–2002. Clin Ther. 2004;26(4):607–614. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy JJ, Maciejewski M, Liu D, Blodgett E. Cost-related nonadherence in the Medicare program: the impact of Part D. Med Care. 2011;49(5):522–526. - PubMed
-
- Soumerai SB, Pierre-Jacques M, Zhang F et al. Cost-related medication nonadherence among elderly and disabled Medicare beneficiaries: a national survey 1 year before the Medicare drug benefit. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(17):1829–1835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous