The HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people in China between 2005 and 2012: results of a spatial temporal analysis
- PMID: 27552922
- PMCID: PMC5354990
- DOI: 10.1111/hiv.12408
The HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people in China between 2005 and 2012: results of a spatial temporal analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Despite a recent increase in the HIV/AIDS epidemic among young people in China, youth-specific HIV data are limited.
Methods: In total, 56 621 individuals with HIV/AIDS, aged 15-24 years, registered in the Case Reporting System of China between 2005 and 2012 and having complete spatial information were included in the present analysis. Spatial autocorrelation (general and local) and space-time scanning were performed using the ArcGIS 10.2 and SaTScan 9.3 software, respectively.
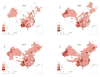
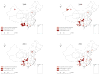
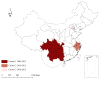
Results: During 2005-2012, the number of reported HIV/AIDS cases and the proportion of HIV cases increased while the proportion of AIDS cases decreased. Sexual contact became the predominant route of transmission in later years. Spatial analysis showed marked geographical variations in HIV infection among young people throughout China during 2005-2012. The number of new hotspots increased over time. They were mainly localized to southeastern coastal areas, southwestern frontier provinces or autonomous regions (of Guangxi, Yunnan and Sichuan) and Beijing municipality. Later these hotspots disappeared and new hotspots were found in the northeast of the country. Significant clusters of HIV-positive cases were identified in three different time periods, which indicated high HIV transmission among young Chinese people in the recent past. The risk of HIV infection was highest in the first cluster (2009-2012; this cluster was the largest in size) covering the provinces of Guizhou and Yunnan, the Chongqing municipality, Guangxi, and the province of Sichuan. The second cluster (2010-2012) was mostly located in Shanghai, South Jiangsu, Zhejiang and South Anhui, while the third cluster (2010-2012) was located in Beijing and Tianjin.
Conclusions: Target-specific comprehensive behavioural interventions are urgently needed to contain the HIV epidemic among young people.
Keywords: HIV; China; cluster; hotspots; spatial analysis; young people.
© 2016 British HIV Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Malaria situation in the People's Republic of China in 2002].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2003;21(4):193-6. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14628361 Chinese.
-
[Spatial-temporal distribution of newly detected HIV/AIDS cases among aged 15 years or older women in China, 2010-2016].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 10;39(6):739-744. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.06.009. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29936739 Chinese.
-
The spatial distribution pattern of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immune deficiency syndrome in China.Geospat Health. 2016 May 31;11(2):414. doi: 10.4081/gh.2016.414. Geospat Health. 2016. PMID: 27245799
-
AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa: the epidemiology of heterosexual transmission and the prospects for prevention.Epidemiology. 1993 Jan;4(1):63-72. Epidemiology. 1993. PMID: 8420583 Review.
-
Injection drug use and HIV/AIDS transmission in China.Cell Res. 2005 Nov-Dec;15(11-12):865-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290360. Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 16354561 Review.
Cited by
-
An Assessment of Trends in HIV-1 Prevalence and Incidence and Spatio-Temporal Analyses of HIV-1 Recent Infection Among MSM During the Surveillance Period Between 2018 and 2022 in Sichuan, China.HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2024 Mar 6;16:83-93. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S448096. eCollection 2024. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38464995 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial, temporal, and spatiotemporal analysis of mumps in Guangxi Province, China, 2005-2016.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Aug 2;18(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3240-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30068308 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and behavior characteristics of individuals who used ketamine.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 17;12(1):801. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-04832-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35039593 Free PMC article.
-
Older adults at high risk of HIV infection in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.PeerJ. 2020 Oct 21;8:e9731. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9731. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33150054 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the college-based HIV/AIDS education policy in Beijing, China: a mixed method approach.Environ Health Prev Med. 2020 Sep 10;25(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12199-020-00890-5. Environ Health Prev Med. 2020. PMID: 32912181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Francis B, Taboada F, Andiorio E, et al. Demonstration of Improved Sensitivity and Specificity in Blood-Donors by a Prototype Hcv-3. 0 Elisa. Transfusion. 1993;33(9):S32–S32.
-
- Riezuboj JI, Parker D, Civeira MP, et al. Detection of Hepatitis-C Virus-Antibodies with New Recombinant Antigens - Assessment in Chronic Liver-Diseases. Journal of Hepatology. 1992;15(3):309–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

