Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds
- PMID: 27552971
- PMCID: PMC5107309
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm.2016.93
Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds
Abstract
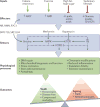
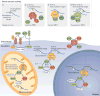
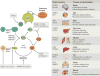
The sirtuins (SIRT1-7) are a family of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent deacylases with remarkable abilities to prevent diseases and even reverse aspects of ageing. Mice engineered to express additional copies of SIRT1 or SIRT6, or treated with sirtuin-activating compounds (STACs) such as resveratrol and SRT2104 or with NAD+ precursors, have improved organ function, physical endurance, disease resistance and longevity. Trials in non-human primates and in humans have indicated that STACs may be safe and effective in treating inflammatory and metabolic disorders, among others. These advances have demonstrated that it is possible to rationally design molecules that can alleviate multiple diseases and possibly extend lifespan in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
statement The authors declare competing interests: see Web version for details.
Figures
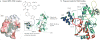
References
-
- McCay CM, Crowell MF, Maynard LA. The effect of retarded growth upon the length of life span and upon the ultimate body size. 1935. Nutrition. 1989;5:155–171. A pioneering study reporting that reduced calorie intake and reduced body size leads to extended longevity. - PubMed
-
- Sinclair DA. Toward a unified theory of caloric restriction and longevity regulation. Mech Ageing Dev. 2005;126:987–1002. - PubMed
-
- Kenyon CJ. The genetics of ageing. Nature. 2010;464:504–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

