Unique quadruple immunofluorescence assay demonstrates mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in osteoblasts of aged and PolgA(-/-) mice
- PMID: 27553587
- PMCID: PMC4995399
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31907
Unique quadruple immunofluorescence assay demonstrates mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in osteoblasts of aged and PolgA(-/-) mice
Abstract
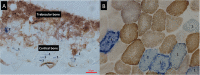
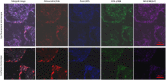
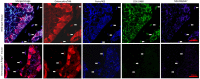
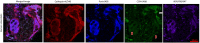
Fragility fractures caused by osteoporosis affect millions of people worldwide every year with significant levels of associated morbidity, mortality and costs to the healthcare economy. The pathogenesis of declining bone mineral density is poorly understood but it is inherently related to increasing age. Growing evidence in recent years, especially that provided by mouse models, suggest that accumulating somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations may cause the phenotypic changes associated with the ageing process including osteoporosis. Methods to study mitochondrial abnormalities in individual osteoblasts, osteoclasts and osteocytes are limited and impair our ability to assess the changes seen with age and in animal models of ageing. To enable the assessment of mitochondrial protein levels, we have developed a quadruple immunofluorescence method to accurately quantify the presence of mitochondrial respiratory chain components within individual bone cells. We have applied this technique to a well-established mouse model of ageing and osteoporosis and show respiratory chain deficiency.
Figures


References
-
- Looker A. C. et al.. Updated data on proximal femur bone mineral levels of US adults. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 8, 468–489 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Kanis J. A. Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk. The Lancet 359, 1929–1936 (2002). - PubMed
-
- van den Bergh J. P., van Geel T. A. & Geusens P. P. Osteoporosis, frailty and fracture: implications for case finding and therapy. Nature reviews. Rheumatology 8, 163–172 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

