The chemical biology of HNO signaling
- PMID: 27555493
- PMCID: PMC5318259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.08.014
The chemical biology of HNO signaling
Abstract
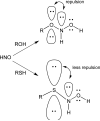
Nitroxyl (HNO) is a simple molecule with significant potential as a pharmacological agent. For example, its use in the possible treatment of heart failure has received recent attention due to its unique therapeutic properties. Recent progress has been made on the elucidation of the mechanisms associated with its biological signaling. Importantly, the biochemical mechanisms described for HNO bioactivity are consistent with its unique and novel chemical properties/reactivity. To date, much of the biology of HNO can be associated with interactions and modification of important regulatory thiol proteins. Herein will be provided a description of HNO chemistry and how this chemistry translates to some of its reported biological effects.
Keywords: Azanone; Nitrogen oxides; Nitroxyl; Thiols.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
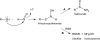

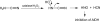
References
-
- Fukuto JM, Carrington SJ. HNO Signaling Mechanisms. Antiox. Redox Signal. 2011;14(9):1649–1657. - PubMed
-
- Irvine JC, Ritchie RH, Favaloro JL, Andrews KL, Widdop RE, Kemp-Harper BK. Nitroxyl (HNO): The Ciderella of the nitric oxide story. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008;29:601–608. - PubMed
-
- Miranda KM, Nagasawa HT, Toscano JP. Donors of HNO. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005;5:649–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

