Protein arginine methylation/demethylation and cancer
- PMID: 27556302
- PMCID: PMC5341895
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11376
Protein arginine methylation/demethylation and cancer
Abstract
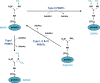
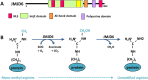
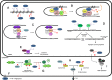
Protein arginine methylation is a common post-translational modification involved in numerous cellular processes including transcription, DNA repair, mRNA splicing and signal transduction. Currently, there are nine known members of the protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family, but only one arginine demethylase has been identified, namely the Jumonji domain-containing 6 (JMJD6). Although its demethylase activity was initially challenged, its dual activity as an arginine demethylase and a lysine hydroxylase is now recognized. Interestingly, a growing number of substrates for arginine methylation and demethylation play key roles in tumorigenesis. Though alterations in the sequence of these enzymes have not been identified in cancer, their overexpression is associated with various cancers, suggesting that they could constitute targets for therapeutic strategies. In this review, we present the recent knowledge of the involvement of PRMTs and JMJD6 in tumorigenesis.
Keywords: JMJD6; PRMT; cancer; demethylation; methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Ambler RP, Rees MW. Epsilon-N-Methyl-lysine in bacterial flagellar protein. Nature. 1959;184:56–57. - PubMed
-
- Murray K. The occurrence of epsilon-n-methyl lysine in histones. Biochemistry. 1964;3:10–15. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin GS, Carnegie PR. Specific enzymic methylation of an arginine in the experimental allergic encephalomyelitis protein from human myelin. Science. 1971;171(3971):579–581. - PubMed
-
- Kakimoto Y, Akazawa S. Isolation and identification of N-G,N-G- and N-G,N’-G-dimethyl-arginine, N-epsilon-mono-, di-, and trimethyllysine, and glucosylgalactosyl- and galactosyl-delta-hydroxylysine from human urine. J Biol Chem. 1970;245(21):5751–5758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

