Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Transanal Irrigation in Patients with Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction
- PMID: 27557052
- PMCID: PMC4996513
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159394
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Transanal Irrigation in Patients with Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction
Abstract
Background: People suffering from neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) and an ineffective bowel regimen often suffer from fecal incontinence (FI) and related symptoms, which have a huge impact on their quality of life. In these situations, transanal irrigation (TAI) has been shown to reduce these symptoms and improve quality of life.
Aim: To investigate the long-term cost-effectiveness of initiating TAI in patients with NBD who have failed standard bowel care (SBC).
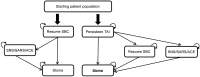
Methods: A deterministic Markov decision model was developed to project the lifetime health economic outcomes, including quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), episodes of FI, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and stoma surgery when initiating TAI relative to continuing SBC. A data set consisting of 227 patients with NBD due to spinal cord injury (SCI), multiple sclerosis, spina bifida and cauda equina syndrome was used in the analysis. In the model a 30-year old individual with SCI was used as a base-case. A probabilistic sensitivity analysis was applied to evaluate the robustness of the model.
Results: The model predicts that a 30-year old SCI patient with a life expectancy of 37 years initiating TAI will experience a 36% reduction in FI episodes, a 29% reduction in UTIs, a 35% reduction in likelihood of stoma surgery and a 0.4 improvement in QALYs, compared with patients continuing SBC. A lifetime cost-saving of £21,768 per patient was estimated for TAI versus continuing SBC alone.
Conclusion: TAI is a cost-saving treatment strategy reducing risk of stoma surgery, UTIs, episodes of FI and improving QALYs for NBD patients who have failed SBC.
Conflict of interest statement
FA and ZS are employees of Coloplast A/S who have funded the study. AE, PC and SK are occasionally used as KOLs for advisory boards at Coloplast A/S. The authors confirm that this does not alter the authors' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
-
- Krogh K, Nielsen J, Djurhuus JC, Mosdal C, Sabroe S, Laurberg S (1997) Colorectal function in patients with spinal cord lesions. Dis Colon Rectum 40: 1233–1239. - PubMed
-
- Verhoef M, Lurvink M, Barf HA, Post MW, van Asbeck FW, Gooskens RH, et al. (2005) High prevalence of incontinence among young adults with spina bifida: description, prediction and problem perception. Spinal Cord 43: 331–340. - PubMed
-
- Hinds JP, Eidelman BH, Wald A (1990) Prevalence of bowel dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. A population survey. Gastroenterology 98: 1538–1542. - PubMed
-
- DeLisa JA, Kirshblum S (1997) A review: frustrations and needs in clinical care of spinal cord injury patients. J Spinal Cord Med 20: 384–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

