An integrative transcriptomic atlas of organogenesis in human embryos
- PMID: 27557446
- PMCID: PMC4996651
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.15657
An integrative transcriptomic atlas of organogenesis in human embryos
Abstract
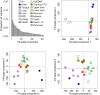
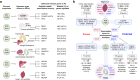
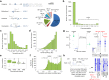
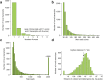
Human organogenesis is when severe developmental abnormalities commonly originate. However, understanding this critical embryonic phase has relied upon inference from patient phenotypes and assumptions from in vitro stem cell models and non-human vertebrates. We report an integrated transcriptomic atlas of human organogenesis. By lineage-guided principal components analysis, we uncover novel relatedness of particular developmental genes across different organs and tissues and identified unique transcriptional codes which correctly predicted the cause of many congenital disorders. By inference, our model pinpoints co-enriched genes as new causes of developmental disorders such as cleft palate and congenital heart disease. The data revealed more than 6000 novel transcripts, over 90% of which fulfil criteria as long non-coding RNAs correlated with the protein-coding genome over megabase distances. Taken together, we have uncovered cryptic transcriptional programs used by the human embryo and established a new resource for the molecular understanding of human organogenesis and its associated disorders.
Keywords: developmental biology; embryo; human; human biology; medicine; organogenesis; rna-seq; stem cells; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures







Comment in
-
How to build a human.Elife. 2016 Aug 24;5:e19826. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19826. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27557445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J. http://bioconductor.org/packages/topGO/ Bioconductor. (topGO: topGO: Enrichment Analysis for Gene Ontology) 2010
-
- Bolstad B. http://bioconductor.org/packages/preprocessCore/ Bioconductor. (preprocessCore: A Collection of Pre-Processing Functions) 2007
-
- Cebola I, Rodríguez-Seguí SA, Cho CH, Bessa J, Rovira M, Luengo M, Chhatriwala M, Berry A, Ponsa-Cobas J, Maestro MA, Jennings RE, Pasquali L, Morán I, Castro N, Hanley NA, Gomez-Skarmeta JL, Vallier L, Ferrer J. TEAD and YAP regulate the enhancer network of human embryonic pancreatic progenitors. Nature Cell Biology. 2015;17:615–626. doi: 10.1038/ncb3160. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

