Exosomes bind to autotaxin and act as a physiological delivery mechanism to stimulate LPA receptor signalling in cells
- PMID: 27557622
- PMCID: PMC5087657
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.184424
Exosomes bind to autotaxin and act as a physiological delivery mechanism to stimulate LPA receptor signalling in cells
Abstract
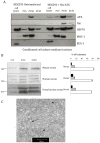
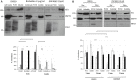
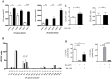
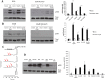
Autotaxin (ATX; also known as ENPP2), the lysophospholipase responsible for generating the lipid receptor agonist lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), is a secreted enzyme. Here we show that, once secreted, ATX can bind to the surface of cell-secreted exosomes. Exosome-bound ATX is catalytically active and carries generated LPA. Once bound to a cell, through specific integrin interactions, ATX releases the LPA to activate cell surface G-protein-coupled receptors of LPA; inhibition of signalling by the receptor antagonist Ki1642 suggests that these receptors are LPAR1 and LPAR3. The binding stimulates downstream signalling, including phosphorylation of AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinases, the release of intracellular stored Ca2+ and cell migration. We propose that exosomal binding of LPA-loaded ATX provides a means of efficiently delivering the lipid agonist to cell surface receptors to promote signalling. We further propose that this is a means by which ATX-LPA signalling operates physiologically.
Keywords: Autotaxin; Exosome; Integrin; LPA.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



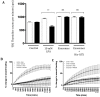
References
-
- Baumforth K. R. N., Flavell J. R., Reynolds G. M., Davies G., Pettit T. R., Wei W., Morgan S., Stankovic T., Kishi Y., Arai H. et al. (2005). Induction of autotaxin by the Epstein-Barr virus promotes the growth and survival of Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Blood 106, 2138-2146. 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0471 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hausmann J., Kamtekar S., Christodoulou E., Day J. E., Wu T., Fulkerson Z., Albers H. M. H. G., van Meeteren L. A., Houben A. J. S., van Zeijl L. et al. (2011). Structural basis of substrate discrimination and integrin binding by autotaxin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 198-204. 10.1038/nsmb.1980 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

