Immunity and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: translating mechanisms to biomarkers and treatment targets
- PMID: 27558558
- PMCID: PMC6109808
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00314.2016
Immunity and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: translating mechanisms to biomarkers and treatment targets
Abstract
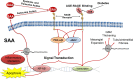
Increasing incidences of obesity and diabetes have made diabetic kidney disease (DKD) the leading cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease worldwide. Despite current pharmacological treatments, including strategies for optimizing glycemic control and inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system, DKD still makes up almost one-half of all cases of end-stage renal disease in the United States. Compelling and mounting evidence has clearly demonstrated that immunity and inflammation play a paramount role in the pathogenesis of DKD. This article reviews the involvement of the immune system in DKD and identifies important roles of key immune and inflammatory mediators. One of the most recently identified biomarkers is serum amyloid A, which appears to be relatively specific for DKD. Novel and evolving treatment approaches target protein kinases, transcription factors, chemokines, adhesion molecules, growth factors, advanced glycation end-products, and other inflammatory molecules. This is the beginning of a new era in the understanding and treatment of DKD, and we may have finally reached a tipping point in our fight against the growing burden of DKD.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic kidney disease; inflammation; treatment.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature : 787–793, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Abbate M, Zoja C, Rottoli D, Corna D, Perico N, Bertani T, Remuzzi G. Antiproteinuric therapy while preventing the abnormal protein traffic in proximal tubule abrogates protein- and complement-dependent interstitial inflammation in experimental renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol : 804–813, 1999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

