Individualized Approaches Are Needed for Optimized Blood Cultures
- PMID: 27558570
- PMCID: PMC5091349
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciw573
Individualized Approaches Are Needed for Optimized Blood Cultures
Abstract
Many strategies and technologies are available to improve blood culture (BC)-based diagnostics. The ideal approach to BCs varies between healthcare institutions. Institutions need to examine clinical needs and practices in order to optimize BC-based diagnostics for their site. Before laboratories consider offering rapid matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF MS) or expensive rapid panel-based molecular BC diagnostics, they should optimize preanalytical, analytical, and postanalytical processes and procedures surrounding BC systems. Several factors need to be considered, including local resistance rates, antibiotic prescribing patterns, patient- and provider-types, laboratory staffing, and personnel available to liaise with clinicians to optimize antibiotic use. While there is much excitement surrounding new high-technology diagnostics, cost-neutral benefits can be realized by optimizing existing strategies and using available tools in creative ways. Rapid BC diagnostics should be implemented in a manner that optimizes impact. Strategies to optimize these BC diagnostics in individual laboratories are presented here.
Keywords: bacteremia; blood culture.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
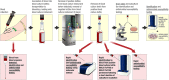
References
-
- Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med 2006; 34:1589–96. - PubMed
-
- Roberts RR, Hota B, Ahmad I et al. Hospital and societal costs of antimicrobial-resistant infections in a Chicago teaching hospital: implications for antibiotic stewardship. Clin Infect Dis 2009; 49:1175–84. - PubMed
-
- Zadroga R, Williams DN, Gottschall R et al. Comparison of 2 blood culture media shows significant differences in bacterial recovery for patients on antimicrobial therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 56:790–7. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Principles and Procedures for Blood Cultures; Approved Guideline Wayne, PA, 2007.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

