Characterization of a protein-protein interaction within the SigO-RsoA two-subunit σ factor: the σ70 region 2.3-like segment of RsoA mediates interaction with SigO
- PMID: 27558998
- PMCID: PMC5903212
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.000358
Characterization of a protein-protein interaction within the SigO-RsoA two-subunit σ factor: the σ70 region 2.3-like segment of RsoA mediates interaction with SigO
Abstract
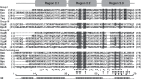
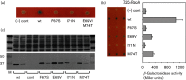
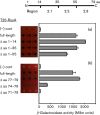
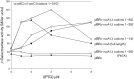
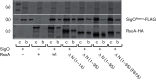
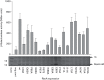
σ factors are single subunit general transcription factors that reversibly bind core RNA polymerase and mediate gene-specific transcription in bacteria. Previously, an atypical two-subunit σ factor was identified that activates transcription from a group of related promoters in Bacillus subtilis. Both of the subunits, named SigO and RsoA, share primary sequence similarity with the canonical σ70 family of σ factors and interact with each other and with RNA polymerase subunits. Here we show that the σ70 region 2.3-like segment of RsoA is unexpectedly sufficient for interaction with the amino-terminus of SigO and the β' subunit. A mutational analysis of RsoA identified aromatic residues conserved amongst all RsoA homologues, and often amongst canonical σ factors, that are particularly important for the SigO-RsoA interaction. In a canonical σ factor, region 2.3 amino acids bind non-template strand DNA, trapping the promoter in a single-stranded state required for initiation of transcription. Accordingly, we speculate that RsoA region 2.3 protein-binding activity likely arose from a motif that, at least in its ancestral protein, participated in DNA-binding interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The atypical two-subunit σ factor from Bacillus subtilis is regulated by an integral membrane protein and acid stress.Microbiology (Reading). 2016 Feb;162(2):398-407. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000223. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Microbiology (Reading). 2016. PMID: 26651345
-
Functional reconstitution of an unusual Firmicutes σ factor into a Gram-negative heterologous host.Can J Microbiol. 2015 Nov;61(11):818-26. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2015-0408. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Can J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26367498
-
A promoter melting region in the primary sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis. Identification of functionally important aromatic amino acids.J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1470-88. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1102. J Mol Biol. 1994. PMID: 8107087
-
Role of the RNA polymerase sigma subunit in transcription initiation.Res Microbiol. 2002 Nov;153(9):557-62. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(02)01368-2. Res Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12455702 Review.
-
How sigma docks to RNA polymerase and what sigma does.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2001 Apr;4(2):126-31. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00177-6. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11282466 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracytoplasmic Function σ Factors as Tools for Coordinating Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 9;22(8):3900. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083900. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expansion and re-classification of the extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factor family.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 25;49(2):986-1005. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1229. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33398323 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic modulation of bacterial resource allocation by perturbing RNA polymerase availability via synthetic transcriptional switches.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Aug 11;53(15):gkaf814. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf814. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40842238 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric MerR-Family Regulators and Logic Elements for the Design of Metal Sensitive Genetic Circuits in Bacillus subtilis.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Mar 17;12(3):735-749. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00545. Epub 2023 Jan 11. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 36629785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banta A. B., Chumanov R. S., Yuan A. H., Lin H., Campbell E. A., Burgess R. R., Gourse R. L.(2013). Key features of σS required for specific recognition by Crl, a transcription factor promoting assembly of RNA polymerase holoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 11015955–15960. 10.1073/pnas.1311642110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhandari V., Ahmod N. Z., Shah H. N., Gupta R. S.(2013). Molecular signatures for Bacillus species: demarcation of the Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus clades in molecular terms and proposal to limit the placement of new species into the genus Bacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 632712–2726. 10.1099/ijs.0.048488-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

