Sex Differences in Mental Stress-Induced Myocardial Ischemia in Patients With Coronary Heart Disease
- PMID: 27559072
- PMCID: PMC5079026
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003630
Sex Differences in Mental Stress-Induced Myocardial Ischemia in Patients With Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
Background: Emerging data suggest that young women with coronary heart disease (CHD) are disproportionally vulnerable to the adverse cardiovascular effects of psychological stress. We hypothesized that younger, but not older, women with stable CHD are more likely than their male peers to develop mental stress-induced myocardial ischemia (MSIMI).
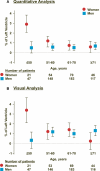
Methods and results: We studied 686 patients (191 women) with stable coronary heart disease (CHD). Patients underwent (99m)Tc-sestamibi myocardial perfusion imaging at rest and with both mental (speech task) and conventional (exercise/pharmacological) stress testing. We compared quantitative (by automated software) and visual parameters of inducible ischemia between women and men and assessed age as an effect modifier. Women had a more-adverse psychosocial profile than men whereas there were few differences in medical history and CHD risk factors. Both quantitative and visual indicators of ischemia with mental stress were disproportionally larger in younger women. For each 10 years of decreasing age, the total reversibility severity score with mental stress was 9.6 incremental points higher (interaction, P<0.001) and the incidence of MSIMI was 82.6% higher (interaction, P=0.004) in women than in men. Incidence of MSIMI in women ≤50 years was almost 4-fold higher than in men of similar age and older patients. These results persisted when adjusting for sociodemographic and medical risk factors, psychosocial factors, and medications. There were no significant sex differences in inducible ischemia with conventional stress.
Conclusions: Young women with stable CHD are susceptible to MSIMI, which could play a role in the prognosis of this group.
Keywords: ischemia; ischemic heart disease; sex differences; stress; women.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

Comment in
-
Mental Stress and Myocardial Ischemia: Young Women at Risk.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Aug 24;5(9):e004196. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004196. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27559073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nabel EG. Heart disease prevention in young women: sounding an alarm. Circulation. 2015;132:989–991. - PubMed
-
- Izadnegahdar M, Singer J, Lee MK, Gao M, Thompson CR, Kopec J, Humphries KH. Do younger women fare worse? Sex differences in acute myocardial infarction hospitalization and early mortality rates over ten years. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2014;23:10–17. - PubMed
-
- Lehto HR, Lehto S, Havulinna AS, Ketonen M, Lehtonen A, Kesaniemi YA, Airaksinen KJ, Salomaa V. Sex differences in short‐ and long‐term case‐fatality of myocardial infarction. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011;26:851–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

