Incidence of AIDS-Defining Opportunistic Infections in a Multicohort Analysis of HIV-infected Persons in the United States and Canada, 2000-2010
- PMID: 27559122
- PMCID: PMC4996145
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiw085
Incidence of AIDS-Defining Opportunistic Infections in a Multicohort Analysis of HIV-infected Persons in the United States and Canada, 2000-2010
Abstract
Background: There are few recent data on the rates of AIDS-defining opportunistic infections (OIs) among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients in care in the United States and Canada.
Methods: We studied HIV-infected participants in 16 cohorts in the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD) during 2000-2010. After excluding 16 737 (21%) with any AIDS-defining clinical events documented before NA-ACCORD enrollment, we analyzed incident OIs among the remaining 63 541 persons, most of whom received antiretroviral therapy during the observation. We calculated incidence rates per 100 person-years of observation (hereafter, "person-years") with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the first occurrence of any OI and select individual OIs during 2000-2003, 2004-2007, and 2008-2010.
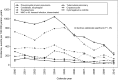
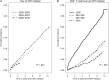
Results: A total of 63 541 persons contributed 261 573 person-years, of whom 5836 (9%) developed at least 1 OI. The incidence rate of any first OI decreased over the 3 observation periods, with 3.0 cases, 2.4 cases, and 1.5 cases per 100 person-years of observation during 2000-2003, 2004-2007, and 2008-2010, respectively (Ptrend<.001); the rates of most individual OIs decreased as well. During 2008-2010, the leading OIs included Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, esophageal candidiasis, and disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex or Mycobacterium kansasii infection.
Conclusions: For HIV-infected persons in care during 2000-2010, rates of first OI were relatively low and generally declined over this time.
Keywords: AIDS-related opportunistic infections; CD4+ T-lymphocyte count; HIV cohort studies; combination antiretroviral therapy; epidemiology; incidence; prophylaxis.
Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures

Comment in
-
Opportunistic Diseases During HIV Infection-Things Aren't What They Used to Be, or Are They?J Infect Dis. 2016 Sep 15;214(6):830-1. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw086. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27559121 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kaplan JE, Hanson D, Dworkin MS et al. Epidemiology of human immunodeficiency virus-associated opportunistic infections in the United States in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 30(suppl 1):S5–14. - PubMed
-
- Moore RD, Chaisson RE. Natural history of HIV infection in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 1999; 13:1933–42. - PubMed
-
- Buchacz K, Baker RK, Palella FJ Jr et al. AIDS-defining opportunistic illnesses in US patients, 1994–2007: a cohort study. AIDS 2010; 24:1549–59. - PubMed
-
- Schwarcz L, Chen M-J, Vittinghoff E, Hsu L, Schwarcz S. Declining incidence of AIDS-defining opportunistic illnesses: results from 16 years of population-based AIDS surveillance. AIDS 2013; 27:597–605. - PubMed
-
- Podlekareva D, Mocroft A, Dragsted UB et al. Factors associated with the development of opportunistic infections in HIV-1-infected adults with high CD4+ cell counts: a EuroSIDA study. J Infect Dis 2006; 194:633–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020790/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY013707/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA165937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- TGF-96118/CIHR/Canada
- Z01 CP010176/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007583/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CBR-94036/CIHR/Canada
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007587/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010121/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008052/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- CBR-86906/CIHR/Canada
- P30 AI110527/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI093197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI065298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA013566/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP055504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002317/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000083/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HCP-97105 /CIHR/Canada
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA037788/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020794/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

