A comparison of the anatomical structure of the pancreas in experimental animals
- PMID: 27559239
- PMCID: PMC4963614
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2016-0016
A comparison of the anatomical structure of the pancreas in experimental animals
Abstract
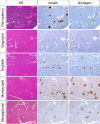
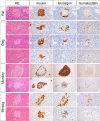
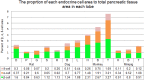
As basic knowledge for evaluation of pancreatic toxicity, anatomical structures were compared among experimental animal species, including rats, dogs, monkeys, and minipigs. In terms of gross anatomy, the pancreases of dogs, monkeys, and minipigs are compact and similar to that of humans. The rat pancreas is relatively compact at the splenic segment, but the duodenal segment is dispersed within the mesentery. In terms of histology, the islet of each animal is characterized by a topographic distribution pattern of α- versus β-cells. β-cells occupy the large central part of the rat islet, and α-cells are located in the periphery and occasionally exhibit cuffing. In dog islets, β-cells are distributed in all parts and α-cells are scattered in the center or periphery of the islet (at body and left lobe); whereas β-cells occupy all parts of the islet and no α-cells are present in the islet (at right lobe). Monkey islets show two distinct patterns, that is, α-cell-rich or β-cell-rich islets, and the former represent peripheral β-cells forming an irregular ring. Minipig islets show an irregular outline, and both α- and β-cells are present in all parts of the islet, intermingling with each other. According to morphometry, the endocrine tissue accounts for <2% of the pancreas roughly in rats and minipigs, and that of monkeys accounts for >7% of the pancreas (at tail). The endocrine tissue proportion tends to increase as the position changes from right to left in the pancreas in each species.
Keywords: endocrine-exocrine interface; extra-insular endocrine cell; pancreas; peri-islet; α-cell; β-cell.
Figures


References
-
- Greaves P. Liver and Pancreas. Endocrine Pancreas. In: Histopathology of Preclinical Toxicity Studies: Interpretation and Relevance in Drug Safety Evaluation, 4th ed. P Greaves (ed). Academic Press, Amsterdam. 501–510. 2012.
-
- Kierszenbaum AL. Endocrine System. In: Histology and Cell Biology: An Introduction to Pathology, 2nd ed. AL Kierszenbaum (ed). Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia. 537–567. 2007.
-
- Kierszenbaum AL. Digestive Glands. In: Histology and Cell Biology: An Introduction to Pathology, 2nd ed. AL Kierszenbaum (ed). Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia. 485–513. 2007.
-
- Cattley RC, Popp JA, and Vonderfecht SL. Liver, Gallbladder, and Exocrine Pancreas. Exocrine Pancreas. In: Toxicologic Pathology: Nonclinical Safety Assessment. PS Sahota, JA Popp, JF Hardisty, and C Gopinath (eds). CRC Press, Boca Raton. 345–356. 2013.
-
- Kui B, Balla Z, Végh ET, Pallagi P, Venglovecz V, Iványi B, Takács T, Hegyi P, and Rakonczay Z., Jr Recent advances in the investigation of pancreatic inflammation induced by large doses of basic amino acids in rodents. Lab Invest. 94: 138–149. 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
