Application of Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition for the design and synthesis of sequence specific probes targeting double-stranded DNA
- PMID: 27559384
- PMCID: PMC4979877
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.12.128
Application of Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition for the design and synthesis of sequence specific probes targeting double-stranded DNA
Abstract
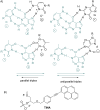
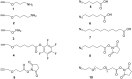
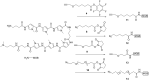
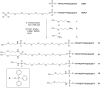
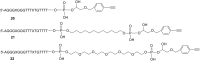
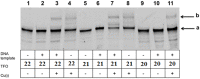
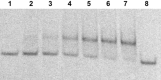
Efficient protocols based on Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition were developed for the synthesis of conjugates of pyrrole-imidazole polyamide minor groove binders (MGB) with fluorophores and with triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs). Diverse bifunctional linkers were synthesized and used for the insertion of terminal azides or alkynes into TFOs and MGBs. The formation of stable triple helices by TFO-MGB conjugates was evaluated by gel-shift experiments. The presence of MGB in these conjugates did not affect the binding parameters (affinity and triplex stability) of the parent TFOs.
Keywords: Cu(I)-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition; binding affinity; click chemistry; pyrrole–imidazole polyamides; sequence specificity: DNA; triplex-forming oligonucleotides.
Figures
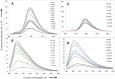
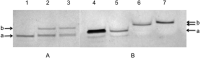
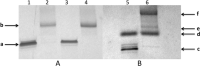
 ” and “
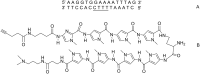
” and “ ”. The duplex is in green, TFO is in black. B) Chemical structure of the TINA molecule inserted in the TFO structure of the DNA triplex as a bulge.
”. The duplex is in green, TFO is in black. B) Chemical structure of the TINA molecule inserted in the TFO structure of the DNA triplex as a bulge.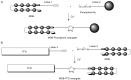

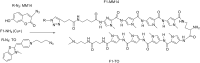

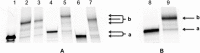
References
-
- Escudé C, Sun J-S. DNA Major Groove Binders: Triple Helix-Forming Oligonucleotides, Triple Helix-Specific DNA Ligands and Cleaving Agents. In: Waring M J, Chaires J B, editors. DNA Binders and Related Subjects. Vol. 253. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2005. pp. 109–148. ((Topics in Current Chemistry)). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
