Management of Tuberculous Infection of the Spine
- PMID: 27559464
- PMCID: PMC4995267
- DOI: 10.4184/asj.2016.10.4.792
Management of Tuberculous Infection of the Spine
Abstract
Spinal tuberculosis accounts for nearly half of all cases of musculoskeletal tuberculosis. It is primarily a medical disease and treatment consists of a multidrug regimen for 9-12 months. Surgery is reserved for select cases of progressive deformity or where neurological deficit is not improved by anti-tubercular treatment. Technology refinements and improved surgical expertise have improved the operative treatment of spinal tuberculosis. The infected spine can be approached anteriorly or posteriorly, in a minimally invasive way. We review the various surgical techniques used in the management of spinal tuberculosis with focus on their indications and contraindications.
Keywords: Anterior instrumentation; Minimal invasive spine surgery; Posterior instrumentation; Posterior only vertebral column resection; Spinal tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




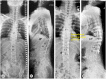
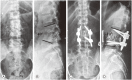
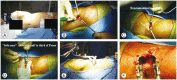
References
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for treatment of tuberculosis [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. [cited 2015 Jul 27]. Available from: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/2010/9789241547833/en/
-
- Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, et al. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:603–662. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

