Evaluation of Adenosine Triphosphate-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 (ABCA1) R219K and C-Reactive Protein Gene (CRP) +1059G/C Gene Polymorphisms in Susceptibility to Coronary Heart Disease
- PMID: 27560308
- PMCID: PMC5003147
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.897104
Evaluation of Adenosine Triphosphate-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 (ABCA1) R219K and C-Reactive Protein Gene (CRP) +1059G/C Gene Polymorphisms in Susceptibility to Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
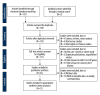
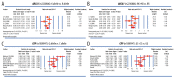
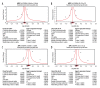
BACKGROUND This meta-analysis investigated the correlation of ABCA1 R219K and C-Reactive Protein Gene (CRP) +1059G/C gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to coronary heart disease (CHD). MATERIAL AND METHODS We searched PubMed, Springer link, Wiley, EBSCO, Ovid, Wanfang database, VIP database, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases to retrieve published studies by keyword. Searches were filtered using our stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria. Resultant high-quality data collected from the final selected studies were analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-analysis 2.0 software. Eleven case-control studies involving 3053 CHD patients and 3403 healthy controls met our inclusion criteria. Seven studies were conducted in Asian populations, 3 studies were done in Caucasian populations, and 1 was in an African population. RESULTS Our major finding was that ABCA1 R219K polymorphism increased susceptibility to CHD in allele model (OR=0.729, 95% CI=0.559~0.949, P=0.019) and dominant model (OR=0.698, 95% CI=0.507~0.961, P=0.027). By contrast, we were unable to find any significant association between the CRP +1059G/C polymorphism and susceptibility to CHD (allele model: OR=1.170, 95% CI=0.782~1.751, P=0.444; dominant model: OR=1.175, 95% CI=0.768~1.797, P=0.457). CONCLUSIONS This meta-analysis provides convincing evidence that polymorphism of ABCA1 R219K is associated with susceptibility to CHD while the CRP +1059G/C polymorphism appears to have no correlation with susceptibility to CHD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ABCA1 rs4149313 polymorphism and susceptibility to coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis.Ann Hum Genet. 2014 Jul;78(4):264-76. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12068. Ann Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24942079
-
The R219K polymorphism on ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 gene is associated with coronary heart disease risk in Asia population: evidence from a meta-analysis.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Jan;71(1):49-55. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0161-8. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25104170
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 R219K polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk in the Chinese population: a meta-analysis.J Neurol Sci. 2014 Jan 15;336(1-2):57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Oct 12. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24157307
-
Association Between ABCA1 R219K Variant and Alzheimer's Disease: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2022;19(10):734-741. doi: 10.2174/1567205020666221114112838. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2022. PMID: 36380407
-
CTLA-4 and MDR1 polymorphisms increase the risk for ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 14;21(34):10025-40. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.10025. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26379408 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of rs2230806 in ABCA1 with coronary artery disease: An updated meta-analysis based on 43 research studies.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(4):e18662. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018662. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 31977856 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Marburg I Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (MI-SNP) and the Marburg II Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (MII-SNP) of the Factor VII-Activating Protease (FSAP) Gene and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): A Pilot Study in a Single Population.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jun 21;24:4271-4278. doi: 10.12659/MSM.906984. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29927903 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of the ABCA1 gene polymorphisms with plasma lipid levels: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(50):e13521. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013521. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30558007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ricke AD, Swiryn S, Bauernfeind RA, et al. Improved pacemaker pulse detection: Clinical evaluation of a new high-bandwidth electrocardiographic system. J Electrocardiol. 2011;44:265–74. - PubMed
-
- Yin YW, Hu AM, Sun QQ, et al. Association between interleukin-6 gene –174 G/C polymorphism and the risk of coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis of 20 studies including 9619 cases and 10,919 controls. Gene. 2012;503:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Tang K, Zhou K, et al. Quantitative assessment of the effect of ABCA1 R219K polymorphism on the risk of coronary heart disease. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:1809–13. - PubMed
-
- Shirai K, Iso H, Ohira T, et al. Perceived level of life enjoyment and risks of cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality: The Japan public health center-based study. Circulation. 2009;120:956–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

