Asthma and Rhinitis Are Associated with Less Objectively-Measured Moderate and Vigorous Physical Activity, but Similar Sport Participation, in Adolescent German Boys: GINIplus and LISAplus Cohorts
- PMID: 27560942
- PMCID: PMC4999273
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161461
Asthma and Rhinitis Are Associated with Less Objectively-Measured Moderate and Vigorous Physical Activity, but Similar Sport Participation, in Adolescent German Boys: GINIplus and LISAplus Cohorts
Abstract
Introduction: Physical activity (PA) protects against most noncommunicable diseases and has been associated with decreased risk of allergic phenotype, which is increasing worldwide. However, the association is not always present; furthermore it is not clear whether it is strongest for asthma, rhinitis, symptoms of these, or atopic sensitization; which sex is most affected; or whether it can be explained by either avoidance of sport or exacerbation of symptoms by exercise. Interventions are thus difficult to target.
Methods: PA was measured by one-week accelerometry in 1137 Germans (mean age 15.6 years, 47% boys) from the GINIplus and LISAplus birth cohorts, and modeled as a correlate of allergic symptoms, sensitization, or reported doctor-diagnosed asthma or rhinitis.
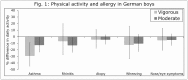
Results: 8.3% of children had asthma, of the remainder 7.9% had rhinitis, and of the remainder 32% were sensitized to aero-allergens (atopic). 52% were lung-healthy controls. Lung-healthy boys and girls averaged 46.4 min and 37.8 min moderate-to-vigorous PA per day, of which 14.6 and 11.4 min was vigorous. PA in allergic girls was not altered, but boys with asthma got 13% less moderate and 29% less vigorous PA, and those with rhinitis with 13% less moderate PA, than lung-healthy boys. Both sexes participated comparably in sport (70 to 84%). Adolescents with wheezing (up to 68%, in asthma) and/or nose/eye symptoms (up to 88%, in rhinitis) were no less active.
Conclusions: We found that asthma and rhinitis, but not atopy, were independently associated with low PA in boys, but not in girls. These results indicate that allergic boys remain a high-risk group for physical inactivity even if they participate comparably in sport. Research into the link between PA and allergy should consider population-specific and sex-specific effects, and clinicians, parents, and designers of PA interventions should specifically address PA in allergic boys to ensure full participation.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded in part by the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research – UFZ, a governmental organization. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sensitization to common allergens and its association with allergic disorders at age 4 years: a whole population birth cohort study.Pediatrics. 2001 Aug;108(2):E33. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.2.e33. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11483843
-
Relation of lung function and current inhalant allergen-specific immunoglobulin E concentrations in adolescents (GINIplus cohort).Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015 Sep;115(3):183-90. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26195441
-
ALLERGIC DISEASES AND ASTHMA IN ADOLESCENTS.Georgian Med News. 2015 Jun;(243):58-62. Georgian Med News. 2015. PMID: 26087732
-
Prevention of allergic disease in childhood: clinical and epidemiological aspects of primary and secondary allergy prevention.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004 Jun;15 Suppl 16:4-5, 9-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2004.0148b.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15125698 Review.
-
[Rhinitis, asthma and sports].Recenti Prog Med. 2003 Jul-Aug;94(7-8):324-9. Recenti Prog Med. 2003. PMID: 12868240 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Association between Allergic Rhinitis and Regular Physical Activity in Adults: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Aug 5;17(16):5662. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17165662. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32764473 Free PMC article.
-
MP-AzeFlu Improves the Quality-of-Life of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis.J Asthma Allergy. 2020 Dec 2;13:633-645. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S277734. eCollection 2020. J Asthma Allergy. 2020. PMID: 33293835 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerometer measured levels of moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity and sedentary time in children and adolescents with chronic disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 22;12(6):e0179429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179429. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28640907 Free PMC article.
-
Factors correlating with serum birch pollen IgE status in pregnant women in Hokkaido, Japan: The Japan Environment and Children's Study (JECS).World Allergy Organ J. 2020 Jul 3;13(6):100128. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100128. eCollection 2020 Jun. World Allergy Organ J. 2020. PMID: 32647557 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic rhinitis and rhinosinusitis synergistically compromise the mental health and health-related quality of life of Korean adults: A nationwide population-based survey.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 11;13(1):e0191115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191115. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29324857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitchell EA, Beasley R, Björkstein B, Crane J, Garcia-Marcos L, Keil U, et al. The association between BMI, vigorous physical activity and television viewing and the risk of symptoms of asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema in children and adolescents: ISAAC Phase Three. Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 2013;43(1):73–84. - PubMed
-
- Sugimoto M, Nagao M, Hosoki K, Togashi K, Fujisawa T. Impact Of Allergic Rhinitis On Physical Activity In Children. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2012;129(2 Suppl.):AB238.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

