Health-related quality of life in mucopolysaccharidosis: looking beyond biomedical issues
- PMID: 27561270
- PMCID: PMC5000418
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-016-0503-2
Health-related quality of life in mucopolysaccharidosis: looking beyond biomedical issues
Abstract
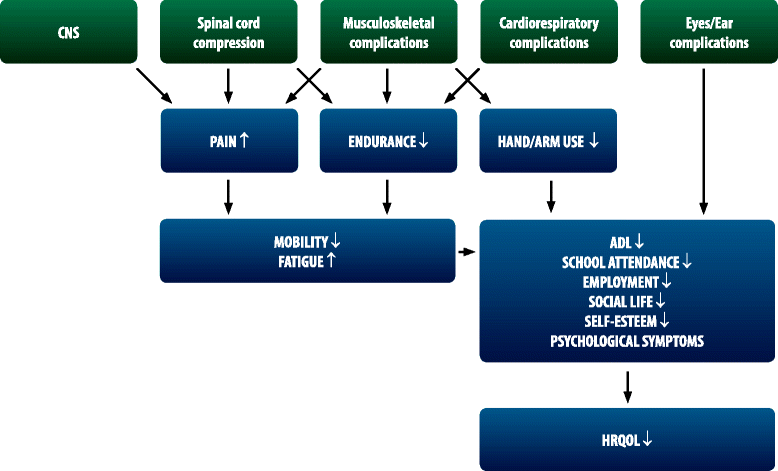
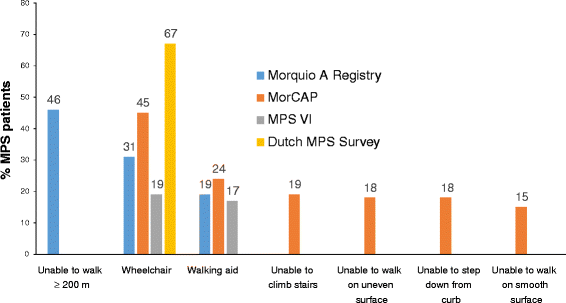
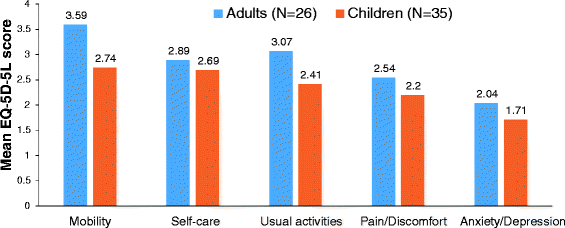
The mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) comprise a heterogeneous family of rare, genetic lysosomal storage disorders that result in severe morbidity and reduced life expectancy. Emerging treatments for several of these disorders have triggered the search for clinically relevant biomarkers and clinical markers associated with treatment efficacy in populations and individuals. However, biomedical measures do not tell the whole story when characterizing a complex chronic disorder such as MPS. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) tools that utilize patient reported outcomes to address patient parameters such as symptoms (pain, fatigue, psychological health), functioning (activity and limitations), or quality of life, have been used to supplement traditional biomedical endpoints. Many of these HRQoL tools have demonstrated that quality of life is negatively impacted in patients with MPS. There is both the opportunity and need to formally standardize and validate HRQoL tools for the different MPS disorders.
Keywords: ADL; Clinical trial; EQ-5D; Enzyme replacement therapy; HRQoL; MPS HAQ; Mucopolysaccharidoses; Pain measurement; Quality of life.
Figures


References
-
- Neufeld EF, Muenzer J. The mucopolysaccharidoses. 2001;8:3421–3452.
-
- Giugliani R, Lampe C, Guffon N, Ketteridge D, Leão-Teles E, Wraith JE, et al. Natural history and galsulfase treatment in mucopolysaccharidosis VI (MPS VI, Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome)-10-year follow-up of patients who previously participated in an MPS VI survey study. Am J Med Genet A. 2014;164A:1953–1964. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36584. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

