Dapagliflozin Enhances Fat Oxidation and Ketone Production in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 27561923
- PMCID: PMC5079607
- DOI: 10.2337/dc15-2688
Dapagliflozin Enhances Fat Oxidation and Ketone Production in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Insulin resistance is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and decreased ATP synthesis. Treatment of individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) improves insulin sensitivity. However, recent reports have demonstrated development of ketoacidosis in subjects with T2DM treated with SGLT2i. The current study examined the effect of improved insulin sensitivity with dapagliflozin on 1) mitochondrial ATP synthesis and 2) substrate oxidation rates and ketone production.
Research design and methods: The study randomized 18 individuals with T2DM to dapagliflozin (n = 9) or placebo (n = 9). Before and after 2 weeks, subjects received an insulin clamp with tritiated glucose, indirect calorimetry, and muscle biopsies.
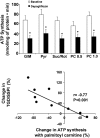
Results: Dapagliflozin reduced fasting plasma glucose (167 ± 13 to 128 ± 6 mg/dL) and increased insulin-stimulated glucose disposal by 36% (P < 0.01). Glucose oxidation decreased (1.06 to 0.80 mg/kg ⋅ min, P < 0.05), whereas nonoxidative glucose disposal (glycogen synthesis) increased (2.74 to 4.74 mg/kg ⋅ min, P = 0.03). Dapagliflozin decreased basal glucose oxidation and increased lipid oxidation and plasma ketone concentration (0.05 to 0.19 mmol/L, P < 0.01) in association with an increase in fasting plasma glucagon (77 ± 8 to 94 ± 13, P < 0.01). Dapagliflozin reduced the ATP synthesis rate, which correlated with an increase in plasma ketone concentration.
Conclusions: Dapagliflozin improved insulin sensitivity and caused a shift from glucose to lipid oxidation, which, together with an increase in glucagon-to-insulin ratio, provide the metabolic basis for increased ketone production.
© 2016 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

References
-
- Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, DeFronzo RA. Role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2011;32:515–531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

