Zinc-sensitive MRI contrast agent detects differential release of Zn(II) ions from the healthy vs. malignant mouse prostate
- PMID: 27562169
- PMCID: PMC5027418
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1609450113
Zinc-sensitive MRI contrast agent detects differential release of Zn(II) ions from the healthy vs. malignant mouse prostate
Abstract
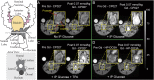
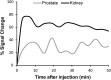
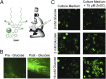
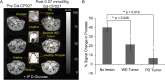
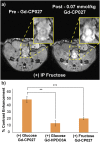
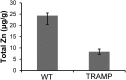
Many secretory tissues release Zn(II) ions along with other molecules in response to external stimuli. Here we demonstrate that secretion of Zn(II) ions from normal, healthy prostate tissue is stimulated by glucose in fasted mice and that release of Zn(II) can be monitored by MRI. An ∼50% increase in water proton signal enhancement is observed in T1-weighted images of the healthy mouse prostate after infusion of a Gd-based Zn(II) sensor and an i.p. bolus of glucose. Release of Zn(II) from intracellular stores was validated in human epithelial prostate cells in vitro and in surgically exposed prostate tissue in vivo using a Zn(II)-sensitive fluorescent probe known to bind to the extracellular surface of cells. Given the known differences in intracellular Zn(II) stores in healthy versus malignant prostate tissues, the Zn(II) sensor was then evaluated in a transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model in vivo. The agent proved successful in detecting small malignant lesions as early as 11 wk of age, making this noninvasive MR imaging method potentially useful for identifying prostate cancer in situations where it may be difficult to detect using current multiparametric MRI protocols.
Keywords: MRI; cancer; glucose; prostate; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D.S., W.-H.L., and C.P. have a financial interest in VitalQuan, LLC.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synchrotron Radiation X-ray Fluorescence Elemental Mapping in Healthy versus Malignant Prostate Tissues Provides New Insights into the Glucose-Stimulated Zinc Trafficking in the Prostate As Discovered by MRI.Inorg Chem. 2019 Oct 21;58(20):13654-13660. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01132. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31260276 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Zinc-Specific iCEST MRI as an Imaging Biomarker for Prostate Cancer.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Oct 21;58(43):15512-15517. doi: 10.1002/anie.201909429. Epub 2019 Sep 17. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31430007 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese(II)-Based Responsive Contrast Agent Detects Glucose-Stimulated Zinc Secretion from the Mouse Pancreas and Prostate by MRI.Inorg Chem. 2021 Feb 15;60(4):2168-2177. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02688. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33507742 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI in detection and staging of prostate cancer.Dan Med J. 2017 Feb;64(2):B5327. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28157066 Review.
-
Role of transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer.Radiol Clin North Am. 2012 Nov;50(6):1061-73. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2012.08.007. Radiol Clin North Am. 2012. PMID: 23122038 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Zinc (Zn) in Human Reproduction: A Journey from Initial Spermatogenesis to Childbirth.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 22;22(4):2188. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042188. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo ZIMIR Imaging of Mouse Pancreatic Islet Cells Shows Oscillatory Insulin Secretion.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 9;12:613964. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.613964. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33767668 Free PMC article.
-
Diketopyrrolopyrrole-based fluorescence probes for the imaging of lysosomal Zn2+ and identification of prostate cancer in human tissue.Chem Sci. 2019 May 1;10(22):5699-5704. doi: 10.1039/c9sc01153f. eCollection 2019 Jun 14. Chem Sci. 2019. PMID: 31293754 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular fMRI of neurochemical signaling.J Neurosci Methods. 2021 Dec 1;364:109372. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2021.109372. Epub 2021 Sep 29. J Neurosci Methods. 2021. PMID: 34597714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc as an Imaging Biomarker of Prostate Cancer.Isr J Chem. 2017 Sep;57(9):854-861. doi: 10.1002/ijch.201700043. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Isr J Chem. 2017. PMID: 30319140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krebs NF. Overview of zinc absorption and excretion in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Nutr. 2000;130(5S Suppl):1374S–1377S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

