Zinc-sensitive MRI contrast agent detects differential release of Zn(II) ions from the healthy vs. malignant mouse prostate
- PMID: 27562169
- PMCID: PMC5027418
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1609450113
Zinc-sensitive MRI contrast agent detects differential release of Zn(II) ions from the healthy vs. malignant mouse prostate
Abstract
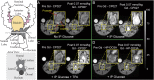
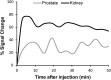
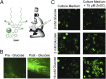
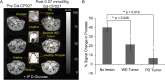
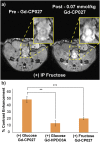
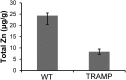
Many secretory tissues release Zn(II) ions along with other molecules in response to external stimuli. Here we demonstrate that secretion of Zn(II) ions from normal, healthy prostate tissue is stimulated by glucose in fasted mice and that release of Zn(II) can be monitored by MRI. An ∼50% increase in water proton signal enhancement is observed in T1-weighted images of the healthy mouse prostate after infusion of a Gd-based Zn(II) sensor and an i.p. bolus of glucose. Release of Zn(II) from intracellular stores was validated in human epithelial prostate cells in vitro and in surgically exposed prostate tissue in vivo using a Zn(II)-sensitive fluorescent probe known to bind to the extracellular surface of cells. Given the known differences in intracellular Zn(II) stores in healthy versus malignant prostate tissues, the Zn(II) sensor was then evaluated in a transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model in vivo. The agent proved successful in detecting small malignant lesions as early as 11 wk of age, making this noninvasive MR imaging method potentially useful for identifying prostate cancer in situations where it may be difficult to detect using current multiparametric MRI protocols.
Keywords: MRI; cancer; glucose; prostate; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
A.D.S., W.-H.L., and C.P. have a financial interest in VitalQuan, LLC.
Figures






References
-
- Krebs NF. Overview of zinc absorption and excretion in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Nutr. 2000;130(5S Suppl):1374S–1377S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

