Stereochemistry Balances Cell Permeability and Solubility in the Naturally Derived Phepropeptin Cyclic Peptides
- PMID: 27563399
- PMCID: PMC4983725
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00100
Stereochemistry Balances Cell Permeability and Solubility in the Naturally Derived Phepropeptin Cyclic Peptides
Abstract
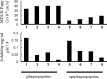
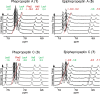
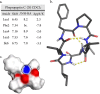
Cyclic peptide (CP) natural products provide useful model systems for mapping "beyond-Rule-of-5" (bRo5) space. We identified the phepropeptins as natural product CPs with potential cell permeability. Synthesis of the phepropeptins and epimeric analogues revealed much more rapid cellular permeability for the natural stereochemical pattern. Despite being more cell permeable, the natural compounds exhibited similar aqueous solubility as the corresponding epimers, a phenomenon explained by solvent-dependent conformational flexibility among the natural compounds. When analyzing the polarity of the solution structures we found that neither the number of hydrogen bonds nor the total polar surface area accurately represents the solvation energies of the high and low dielectric conformations. This work adds to a growing number of natural CPs whose solvent-dependent conformational behavior allows for a balance between aqueous solubility and cell permeability, highlighting structural flexibility as an important consideration in the design of molecules in bRo5 chemical space.
Keywords: bRo5; cyclic peptide; epimer; phepropeptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): R.S.L. is a founder of Circle Pharma.
Figures


References
-
- Yamagishi Y.; Shoji I.; Miyagawa S.; Kawakami T.; Katoh T.; Goto Y.; Suga H. Natural Product-like Macrocyclic N-Methyl-Peptide Inhibitors against a Ubiquitin Ligase Uncovered from a Ribosome-Expressed de Novo Library. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18 (12), 1562–1570. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.09.013. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

