Aptamer and its applications in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 27563707
- PMCID: PMC11107737
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2345-4
Aptamer and its applications in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
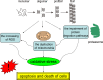
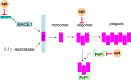
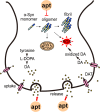
Aptamers are small single-stranded DNA or RNA oligonucleotide fragments or small peptides, which can bind to targets by high affinity and specificity. Because aptamers are specific, non-immunogenic and non-toxic, they are ideal materials for clinical applications. Neurodegenerative disorders are ravaging the lives of patients. Even though the mechanism of these diseases is still elusive, they are mainly characterized by the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the central nervous system. So it is essential to develop potential measures to slow down or prevent the onset of these diseases. With the advancements of the technologies, aptamers have opened up new areas in this research field. Aptamers could bind with these related target proteins to interrupt their accumulation, subsequently blocking or preventing the process of neurodegenerative diseases. This review presents recent advances in the aptamer generation and its merits and limitations, with emphasis on its applications in neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy, Huntington's disease and multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Aptamer; Huntington’s disease; Multiple sclerosis; Neurodegenerative diseases; Parkinson’s disease; Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleic acid aptamers for neurodegenerative diseases.Biochimie. 2018 Feb;145:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.10.026. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 29104136 Review.
-
Chaperones as Potential Pharmacological Targets for Treating Protein Aggregation Illness.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025;26(6):451-466. doi: 10.2174/0113892037338028241230092414. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025. PMID: 39871559 Review.
-
Aptamers targeting amyloidogenic proteins and their emerging role in neurodegenerative diseases.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jan;298(1):101478. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101478. Epub 2021 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 34896392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential roles of natural products in the targeting of proteinopathic neurodegenerative diseases.Neurochem Int. 2021 May;145:105011. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105011. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 33711400 Review.
-
Therapeutic strategies for targeting neurodegenerative protein misfolding disorders.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Jun;44:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.05.018. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29902695 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-Guided Brain Drug Delivery: Expanding the Therapeutic Approach to Neurodegenerative Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 8;13(11):1897. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111897. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prospective approach for aptamers applied in the treatment and molecular diagnostics of ischemic stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1553337. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1553337. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40376266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamers' Potential to Fill Therapeutic and Diagnostic Gaps.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 12;17(1):105. doi: 10.3390/ph17010105. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256938 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex-based aptamers against protein targets in therapy and diagnostics.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt B):1429-1447. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.11.027. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27865995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fighting the Huntington's Disease with a G-Quadruplex-Forming Aptamer Specifically Binding to Mutant Huntingtin Protein: Biophysical Characterization, In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094804. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563194 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

