Cranial Morphology of the Carboniferous-Permian Tetrapod Brachydectes newberryi (Lepospondyli, Lysorophia): New Data from µCT
- PMID: 27563722
- PMCID: PMC5001628
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161823
Cranial Morphology of the Carboniferous-Permian Tetrapod Brachydectes newberryi (Lepospondyli, Lysorophia): New Data from µCT
Abstract
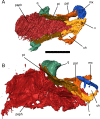
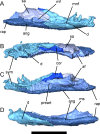
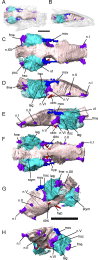
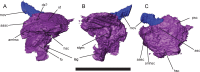
Lysorophians are a group of early tetrapods with extremely elongate trunks, reduced limbs, and highly reduced skulls. Since the first discovery of this group, general similarities in outward appearance between lysorophians and some modern lissamphibian orders (specifically Urodela and Gymnophiona) have been recognized, and sometimes been the basis for hypotheses of lissamphibian origins. We studied the morphology of the skull, with particular emphasis on the neurocranium, of a partial growth series of the lysorophian Brachydectes newberryi using x-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT). Our study reveals similarities between the braincase of Brachydectes and brachystelechid recumbirostrans, corroborating prior work suggesting a close relationship between these taxa. We also describe the morphology of the epipterygoid, stapes, and quadrate in this taxon for the first time. Contra the proposals of some workers, we find no evidence of expected lissamphibian synapomorphies in the skull morphology in Brachydectes newberryi, and instead recognize a number of derived amniote characteristics within the braincase and suspensorium. Morphology previously considered indicative of taxonomic diversity within Lysorophia may reflect ontogenetic rather than taxonomic variation. The highly divergent morphology of lysorophians represents a refinement of morphological and functional trends within recumbirostrans, and is analogous to morphology observed in many modern fossorial reptiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



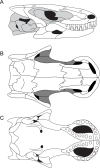
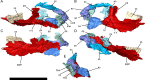
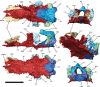


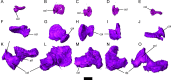



Similar articles
-
Cranial Morphology of the Brachystelechid 'Microsaur' Quasicaecilia texana Carroll Provides New Insights into the Diversity and Evolution of Braincase Morphology in Recumbirostran 'Microsaurs'.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 24;10(6):e0130359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130359. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26107260 Free PMC article.
-
Stem caecilian from the Triassic of Colorado sheds light on the origins of Lissamphibia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 3;114(27):E5389-E5395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706752114. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28630337 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-CT Study of Rhynchonkos stovalli (Lepospondyli, Recumbirostra), with Description of Two New Genera.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 10;10(6):e0127307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127307. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26061187 Free PMC article.
-
A new fossil from the Jurassic of Patagonia reveals the early basicranial evolution and the origins of Crocodyliformes.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2013 Nov;88(4):862-72. doi: 10.1111/brv.12030. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2013. PMID: 23445256 Review.
-
Early tetrapod relationships revisited.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2003 May;78(2):251-345. doi: 10.1017/s1464793102006103. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2003. PMID: 12803423 Review.
Cited by
-
Mandibular musculature constrains brain-endocast disparity between sarcopterygians.R Soc Open Sci. 2020 Sep 23;7(9):200933. doi: 10.1098/rsos.200933. eCollection 2020 Sep. R Soc Open Sci. 2020. PMID: 33047053 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeny of Paleozoic limbed vertebrates reassessed through revision and expansion of the largest published relevant data matrix.PeerJ. 2019 Jan 4;6:e5565. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5565. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30631641 Free PMC article.
-
Hidden morphological diversity among early tetrapods.Nature. 2017 Jun 29;546(7660):642-645. doi: 10.1038/nature22966. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28636600
-
Cranial osteology and neuroanatomy of the late Permian reptile Milleropsis pricei and implications for early reptile evolution.R Soc Open Sci. 2025 Jan 8;12(1):241298. doi: 10.1098/rsos.241298. eCollection 2025 Jan. R Soc Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 39780968 Free PMC article.
-
New material of the 'microsaur' Llistrofus from the cave deposits of Richards Spur, Oklahoma and the paleoecology of the Hapsidopareiidae.PeerJ. 2019 Jan 25;7:e6327. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6327. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30701139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maddin HC, Anderson JS (2012) Evolution of the amphibian ear with implications for lissamphibian phylogeny: insight gained from the caecilian inner ear. Fieldiana Life and Earth Sciences 5: 56–76.
-
- Ruta M, Coates MI (2007) Dates, nodes and character conflict: addressing the lissamphibian origin problem. J Syst Paleontol 5: 69–122.
-
- Sigurdsen T, Green DM (2011) The origin of modern amphibians: a re-evaluation. Zool J Linn Soc 162: 457–469.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

