CD64-directed microtubule associated protein tau kills leukemic blasts ex vivo
- PMID: 27564103
- PMCID: PMC5341865
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11568
CD64-directed microtubule associated protein tau kills leukemic blasts ex vivo
Abstract
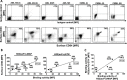
Fc gamma receptor I (FcγRI, CD64) is a well-known target antigen for passive immunotherapy against acute myeloid leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. We recently reported the preclinical immunotherapeutic potential of microtubule associated protein tau (MAP) against a variety of cancer types including breast carcinoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma. Here we demonstrate that the CD64-directed human cytolytic fusion protein H22(scFv)-MAP kills ex vivo 15-50% of CD64+ leukemic blasts derived from seven myeloid leukemia patients. Furthermore, in contrast to the nonspecific cytostatic agent paclitaxel, H22(scFv)-MAP showed no cytotoxicity towards healthy CD64+ PBMC-derived cells and macrophages. The targeted delivery of this microtubule stabilizing agent therefore offers a promising new strategy for specific treatment of CD64+ leukemia.
Keywords: Fc-gamma receptor (CD64); cytolytic fusion proteins; immunotherapy; microtubule associated protein tau (MAP); myeloid leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
DH, RM, TT, and SB are co-inventors on a patent describing H22(scFv)-MAP, which is assigned to Fraunhofer IME. The authors otherwise declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

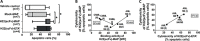

Similar articles
-
Human MAP Tau Based Targeted Cytolytic Fusion Proteins.Biomedicines. 2017 Jun 27;5(3):36. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines5030036. Biomedicines. 2017. PMID: 28653985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granzyme M as a novel effector molecule for human cytolytic fusion proteins: CD64-specific cytotoxicity of Gm-H22(scFv) against leukemic cells.Cancer Lett. 2013 Dec 1;341(2):178-85. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23973499
-
Granzyme B-H22(scFv), a human immunotoxin targeting CD64 in acute myeloid leukemia of monocytic subtypes.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Sep;7(9):2924-32. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0554. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18790773
-
Targeted ex vivo reduction of CD64-positive monocytes in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and acute myelomonocytic leukemia using human granzyme B-based cytolytic fusion proteins.Int J Cancer. 2014 Sep 15;135(6):1497-508. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28786. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24523193
-
Fcgamma receptor 1 (CD64), a target beyond cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(23):2712-8. doi: 10.2174/138161209788923967. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19689341 Review.
Cited by
-
CD64: An Attractive Immunotherapeutic Target for M1-type Macrophage Mediated Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Biomedicines. 2017 Sep 12;5(3):56. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines5030056. Biomedicines. 2017. PMID: 28895912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, optimization, production and activity testing of recombinant immunotoxins expressed in plants and plant cells for the treatment of monocytic leukemia.Bioengineered. 2023 Dec;14(1):2244235. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2023.2244235. Bioengineered. 2023. PMID: 37598369 Free PMC article.
-
Human MAP Tau Based Targeted Cytolytic Fusion Proteins.Biomedicines. 2017 Jun 27;5(3):36. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines5030036. Biomedicines. 2017. PMID: 28653985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Antibody-Drug Conjugate That Selectively Targets Human Monocyte Progenitors for Anti-Cancer Therapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 22;12:618081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.618081. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33692791 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the high affinity receptor, FcγRI, in autoimmune disease, neuropathy, and cancer.Immunother Adv. 2022 May 28;2(1):ltac011. doi: 10.1093/immadv/ltac011. eCollection 2022. Immunother Adv. 2022. PMID: 36284837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Grosso DA, Hess RC, Weiss MA. Immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 2015;121:2689–2704. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

