Preclinical investigation of ibrutinib, a Bruton's kinase tyrosine (Btk) inhibitor, in suppressing glioma tumorigenesis and stem cell phenotypes
- PMID: 27564106
- PMCID: PMC5342527
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11572
Preclinical investigation of ibrutinib, a Bruton's kinase tyrosine (Btk) inhibitor, in suppressing glioma tumorigenesis and stem cell phenotypes
Abstract
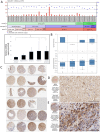
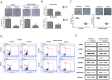
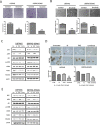
Standard interventions for glioma include surgery, radiation and chemotherapies but the prognosis for malignant cases such as glioblastoma multiforme remain grim. Even with targeted therapeutic agent, bevacitumab, malignant glioma often develops resistance and recurrence. Thus, developing alternative interventions (therapeutic targets, biomarkers) is urgently required. Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) has been long implicated in B cell malignancies but surprisingly it has recently been shown to also play a tumorigenic role in solid tumors such as ovarian and prostate cancer. Bioinformatics data indicates that Btk is significantly higher in clinical glioma samples as compared to normal brain cells and Btk expression level is associated with stage progression. This prompts us to investigate the potential role of Btk as a therapeutic target for glioma. Here, we demonstrate Btk expression is associated with GBM tumorigenesis. Down-regulation of Btk in GBM cell lines showed a significantly reduced abilities in colony formation, migration and GBM sphere-forming potential. Mechanistically, Btk-silenced cells showed a concomitant reduction in the expression of CD133 and Akt/mTOR signaling. In parallel, Ibrutinib (a Btk inhibitor) treatment led to a similar anti-tumorigenic response. Using xenograft mouse model, tumorigenesis was significantly reduced in Btk-silenced or ibrutinib-treated mice as compared to control counterparts. Finally, our glioma tissue microarray analysis indicated a higher Btk staining in the malignant tumors than less malignant and normal brain tissues. Collectively, Btk may represent a novel therapeutic target for glioma and ibrunitib may be used as an adjuvant treatment for malignant GBM.
Keywords: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; cancer stem cells; glioma; ibrutinib.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High expression of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is required for EGFR-induced NF-κB activation and predicts poor prognosis in human glioma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 25;36(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0600-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28946903 Free PMC article.
-
The Development and Applications of a Dual Optical Imaging System for Studying Glioma Stem Cells.Mol Imaging. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1536012119870899. doi: 10.1177/1536012119870899. Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31478435 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) inhibitor ibrutinib suppresses stem-like traits in ovarian cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13255-68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3658. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26036311 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) as a promising target in solid tumors.Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Jul;58:41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017. PMID: 28641100 Review.
-
Current Status of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Development and Use in B-Cell Malignancies.Drugs Aging. 2017 Jul;34(7):509-527. doi: 10.1007/s40266-017-0468-4. Drugs Aging. 2017. PMID: 28536906 Review.
Cited by
-
Periarteriolar Glioblastoma Stem Cell Niches Express Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche Proteins.J Histochem Cytochem. 2018 Mar;66(3):155-173. doi: 10.1369/0022155417749174. Epub 2018 Jan 3. J Histochem Cytochem. 2018. PMID: 29297738 Free PMC article.
-
Ibrutinib Inhibits BTK Signaling in Tumor-Infiltrated B Cells and Amplifies Antitumor Immunity by PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade for Metastatic Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;15(8):2356. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082356. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190284 Free PMC article.
-
Specific Expression of a New Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Isoform (p65BTK) in the Glioblastoma Gemistocytic Histotype.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jan 24;12:2. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00002. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30733667 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Treatment with Acalabrutinib and Rapamycin Inhibits Glioma Stem Cells and Promotes Vascular Normalization by Downregulating BTK/mTOR/VEGF Signaling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 29;14(9):876. doi: 10.3390/ph14090876. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577576 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is required for EGFR-induced NF-κB activation and predicts poor prognosis in human glioma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 25;36(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0600-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28946903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Kerby T, Calvert H. Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2585–2597. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

