Chloroplast-associated metabolic functions influence the susceptibility of maize to Ustilago maydis
- PMID: 27564650
- PMCID: PMC6638283
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12485
Chloroplast-associated metabolic functions influence the susceptibility of maize to Ustilago maydis
Abstract
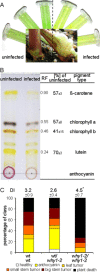
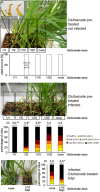
Biotrophic fungal pathogens must evade or suppress plant defence responses to establish a compatible interaction in living host tissue. In addition, metabolic changes during disease reflect both the impact of nutrient acquisition by the fungus to support proliferation and the integration of metabolism with the plant defence response. In this study, we used transcriptome analyses to predict that the chloroplast and associated functions are important for symptom formation by the biotrophic fungus Ustilago maydis on maize. We tested our prediction by examining the impact on disease of a genetic defect (whirly1) in chloroplast function. In addition, we examined whether disease was influenced by inhibition of glutamine synthetase by glufosinate (impacting amino acid biosynthesis) or inhibition of 3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase by glyphosate (influencing secondary metabolism). All of these perturbations increased the severity of disease, thus suggesting a contribution to resistance. Overall, these findings provide a framework for understanding the components of host metabolism that benefit the plant versus the pathogen during a biotrophic interaction. They also reinforce the emerging importance of the chloroplast as a mediator of plant defence.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; Zea mays; maize; photosynthesis; smut; starch; transcription factor.
© 2016 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcripts and tumors: regulatory and metabolic programming during biotrophic phytopathogenesis.F1000Res. 2018 Nov 19;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1812. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.16404.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30519451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maize susceptibility to Ustilago maydis is influenced by genetic and chemical perturbation of carbohydrate allocation.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Dec;18(9):1222-1237. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12486. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27564861 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of ApB73, a virulence factor important for colonization of Zea mays by the smut Ustilago maydis.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Dec;17(9):1467-1479. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12442. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27279632 Free PMC article.
-
The core effector Cce1 is required for early infection of maize by Ustilago maydis.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Oct;19(10):2277-2287. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12698. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29745456 Free PMC article.
-
Ustilago maydis as a Pathogen.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2009;47:423-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081923. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2009. PMID: 19400641 Review.
Cited by
-
The RING-finger ubiquitin E3 ligase TaPIR1 targets TaHRP1 for degradation to suppress chloroplast function.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 12;15(1):6905. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51249-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39134523 Free PMC article.
-
Transcripts and tumors: regulatory and metabolic programming during biotrophic phytopathogenesis.F1000Res. 2018 Nov 19;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1812. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.16404.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30519451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WHIRLY protein functions in plants.Food Energy Secur. 2022 Mar 17;12(2):e379. doi: 10.1002/fes3.379. eCollection 2023 Mar. Food Energy Secur. 2022. PMID: 38440693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary analysis of chloroplast tRNA of Gymnosperm revealed the novel structural variation and evolutionary aspect.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 25;8:e10312. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10312. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33304650 Free PMC article.
-
WHIRLY1 regulates aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis in early seedling development of Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2025 Jan;121(1):e17181. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17181. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 39625871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asselin, J.A. , Lin, J. , Perez‐Quintero, A.L. , Gentzel, I. , Majerczak, D. , Opiyo, S.O. , Zhao, W. , Paek, S.M. , Kim, M.G. , Coplin, D.L. , Blakeslee, J.J. and Mackey, D. (2015) Perturbation of maize phenylpropanoid metabolism by an AvrE family type III effector from Pantoea stewartii . Plant Physiol. 167, 1117–1135. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baley, G.J. , Campbell, K.G. , Yenish, J. , Kidwell, K.K. and Paulitz, T.C. (2009) Influence of glyphosate, crop volunteer and root pathogens on glyphosate‐resistant wheat under controlled environmental conditions. Pest Manag. Sci. 65, 288–299. - PubMed
-
- Bolton, M.D. (2009) Primary metabolism and plant defense–fuel for the fire. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 22, 487–497. - PubMed
-
- Brefort, T. , Doehlemann, G. , Mendoza‐Mendoza, A. , Reissmann, S. , Djamei, A. and Kahmann, R. (2009) Ustilago maydis as a pathogen. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 47, 423–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

