Time required to review research protocols at 10 Veterans Affairs Institutional Review Boards
- PMID: 27565086
- PMCID: PMC7224356
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.06.004
Time required to review research protocols at 10 Veterans Affairs Institutional Review Boards
Abstract
Background: Despite perceptions that institutional review boards (IRBs) delay research, little is known about how long it takes to secure IRB approval. We retrospectively quantified IRB review times at 10 large Veterans Affairs (VA) IRBs.
Methods: We collected IRB records pertaining to a stratified random sample of research protocols drawn from 10 of the 26 largest VA IRBs. Two independent analysts abstracted dates from the IRB records, from which we calculated overall and incremental review times. We used multivariable linear regression to assess variation in total and incremental review times by IRB and review level (i.e., exempt, expedited, or full board) and to identify potential targets for efforts to improve the efficiency and uniformity of the IRB review process.
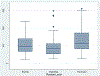
Results: In a sample of 277 protocols, the mean review time was 112 d (95% confidence interval [CI]: 105-120). Compared with full-board reviews at IRB 1, average review times at IRBs 3, 8, 9, and 10 were 27 (95% CI: 6-48), 37 (95% CI: 11-63), 45 (95% CI: 20-69), and 24 (95% CI: 2-45) d shorter, and at IRB 6, times were 56 (95% CI: 28-84) d longer. Across all IRBs, expedited reviews were 44 (95% CI: 30-58) d shorter on average than were full-board reviews, with no significant difference between exempt and full-board reviews. However, after subtracting the time required for Research and Development Committee review, exempt reviews were 21 (95% CI: 1-41) d shorter on average than were full-board reviews.
Conclusions: IRB review times differ significantly by IRB and review level. Few VA IRBs approach a consensus panel goal of 60 d for IRB review. The unexpectedly longer review times for exempt protocols in the VA can be attributed to time required for Research and Development Committee review. Prospective, routine collection of key time points in the IRB review process could inform IRB-specific initiatives for reducing VA IRB review times.
Keywords: Efficiency; Ethics committee; Quality improvement.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research The Belmont Report: Ethical Pricniples and Guidelines for the Protection of Human Subjects of Research. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, 1979.
-
- Emanuel EJ, Wendler D, Grady C What makes clinical research ethical? JAMA 2000:283:2701–2711. - PubMed
-
- Driscoll A, Currey J, Worrall-Carter L, Stewart S Ethical dilemmas of a large national multi-centre study in Australia: time for some consistency. J Clin Nurs 2008:17:2212–2220. - PubMed
-
- Dyrbye LN, Thomas MR, Mechaber AJ, Eacker A, Harper W, et al. Medical education research and IRB review: an analysis and comparison of the IRB review process at six institutions. Acad Med 2007:82:654–660. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources