Investigating the patterns and determinants of seasonal variation in vitamin D status in Australian adults: the Seasonal D Cohort Study
- PMID: 27565723
- PMCID: PMC5002142
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-3582-z
Investigating the patterns and determinants of seasonal variation in vitamin D status in Australian adults: the Seasonal D Cohort Study
Abstract
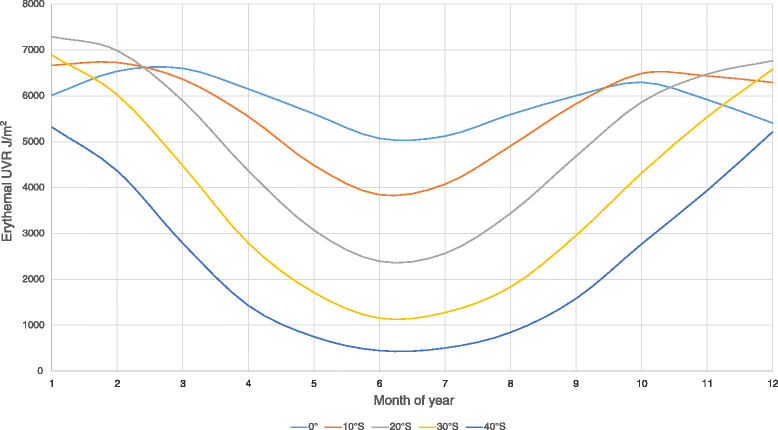
Background: Vitamin D status generally varies seasonally with changing solar UVB radiation, time in the sun, amount of skin exposed, and, possibly, diet. The Seasonal D Study was designed to quantify the amplitude and phase of seasonal variation in the serum concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, (25OH)D)) and identify the determinants of the amplitude and phase and those of inter-individual variability in seasonal pattern.
Methods: The Seasonal D Study collected data 2-monthly for 12 months, including demographics, personal sun exposure using a diary and polysulphone dosimeters over 7 days, and blood for serum 25(OH)D concentration. The study recruited 333 adults aged 18-79 years living in Canberra (35°S, n = 168) and Brisbane (27°South, n = 165), Australia.
Discussion: We report the study design and cohort description for the Seasonal D Study. The study has collected a wealth of data to examine inter- and intra-individual seasonal variation in vitamin D status and serum 25(OH)D levels in Australian adults.
Keywords: Adult; Australia; Cohort; Determinants; Season; Vitamin D.
Figures
References
-
- Kimlin MG, Lucas RM, Harrison SL, van der Mei I, Armstrong BK, Whiteman DC, et al. The contributions of solar ultraviolet radiation exposure and other determinants to serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in Australian adults: the AusD Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;179(7):864–874. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwt446. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McKenzie R, Bodeker G, Keep D, Kothamp M. UV Radiation in New Zealand: North-to-South differences between two sites and relationship to other latitudes. Weather Climate. 1996;16(1):17–26.
-
- Xiang F, Harrison S, Nowak M, Kimlin M, Van der Mei I, Neale RE, et al. Weekend personal ultraviolet radiation exposure in four cities in Australia: influence of temperature, humidity and ambient ultraviolet radiation. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015;143:74–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.12.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical