Small RNA and degradome profiling reveals miRNA regulation in the seed germination of ancient eudicot Nelumbo nucifera
- PMID: 27565736
- PMCID: PMC5002175
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-3032-4
Small RNA and degradome profiling reveals miRNA regulation in the seed germination of ancient eudicot Nelumbo nucifera
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in plant growth and development. MiRNAs and their targets have been widely studied in model plants, but limited knowledge is available concerning this small RNA population and their targets in sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.).
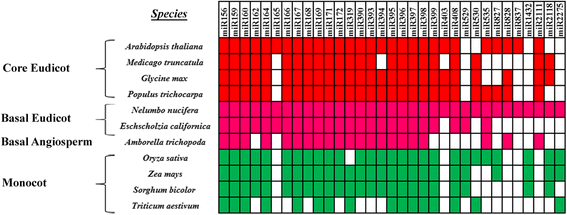
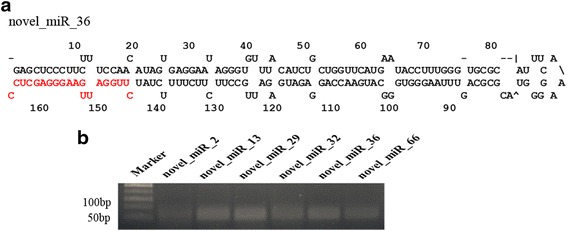
Results: In this study, a total of 145 known miRNAs belonging to 47 families and 78 novel miRNAs were identified during seed germination using high-throughput small RNA sequencing. Furthermore, some miRNA families which have not yet been reported in monocot or eudicot species were detected in N. nucifera, indicating that these miRNAs was divergence from monocots and core eudicots during evolution. Using degradome sequencing, 2580 targets were detected for all the miRNAs. GO (Gene Ontology) and KEGG pathway analyses showed that many target genes enriched in "regulation of transcription" and involved in "carbohydrate", "amino acid and energy metabolism". Nine miRNAs and three corresponding targets of them were further validated by quantitative RT-PCR.
Conclusions: The results present here suggested that many miRNAs were involved in the regulation of seed germination of sacred lotus, providing a foundation for future studies of sacred lotus seed longevity. Comparative analysis of miRNAs from different plants also provided insight into the evolutionary gains and losses of miRNAs in plants.
Keywords: Degradome sequencing; Nelumbo nucifera; Quantitative qRT-PCR; Target genes; miRNA.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Latest Studies on Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)-an Emerging Horticultural Model Plant.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 27;20(15):3680. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153680. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of plant microRNAs: insights from a basal eudicot sacred lotus.Plant J. 2017 Feb;89(3):442-457. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13394. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 27743419
-
Small RNA and Transcriptome Sequencing Reveals miRNA Regulation of Floral Thermogenesis in Nelumbo nucifera.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 8;21(9):3324. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093324. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397143 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and functional analyses of Nelumbo nucifera annexins involved in seed thermotolerance and germination vigor.Planta. 2012 Jun;235(6):1271-88. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1573-y. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Planta. 2012. PMID: 22167260
-
Too Many False Targets for MicroRNAs: Challenges and Pitfalls in Prediction of miRNA Targets and Their Gene Ontology in Model and Non-model Organisms.Bioessays. 2019 Apr;41(4):e1800169. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800169. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 30919506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Submergence-Responsive MicroRNAs and Their Targets Reveals Complex MiRNA-Mediated Regulatory Networks in Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn).Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 18;8:6. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00006. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28149304 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated mRNA and microRNA transcriptome analysis reveals miRNA regulation in response to PVA in potato.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 5;7(1):16925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17059-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29208970 Free PMC article.
-
Barley Seeds miRNome Stability during Long-Term Storage and Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4315. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094315. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919202 Free PMC article.
-
The Latest Studies on Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)-an Emerging Horticultural Model Plant.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 27;20(15):3680. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153680. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid sequence and functional diversification of a miRNA superfamily targeting calcium signaling components in seed plants.New Phytol. 2022 Aug;235(3):1082-1095. doi: 10.1111/nph.18185. Epub 2022 May 21. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35485957 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

