Research interest and activity among medical students in Gothenburg, Sweden, a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 27565878
- PMCID: PMC5002212
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-016-0749-3
Research interest and activity among medical students in Gothenburg, Sweden, a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The proportion of physicians undertaking doctoral studies is decreasing. Early recruitment of medical students could counteract this trend. This follow-up survey investigated research interest and activity among medical students at the Sahlgrenska Academy, Gothenburg, Sweden.
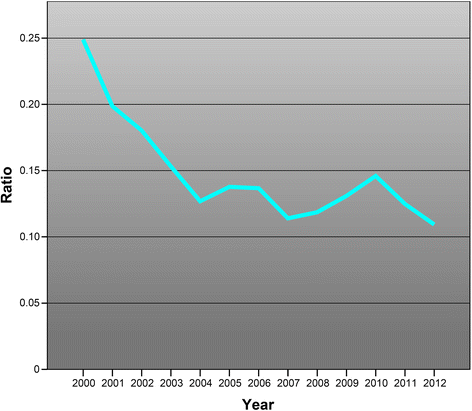
Methods: A questionnaire was administered to all medical students at the Sahlgrenska Academy, as a follow-up to a 2006 survey. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for ordinal variables and the Fisher exact test for categorical variables. Data from Statistics Sweden was used to analyse the number of PhDs awarded to individuals who earned a medical degree in 2000-2012.
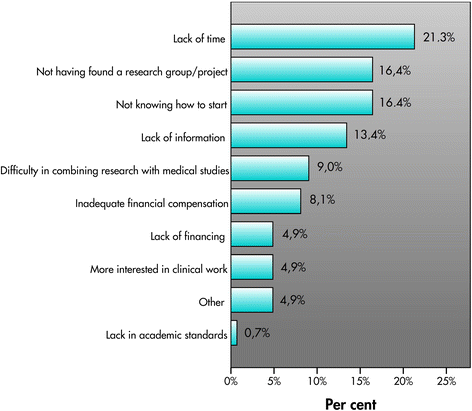
Results: Of the students, 16 % were already conducting and another 36 % wanted to conduct research during their studies. The interest was at the same level compared to 2006. The main reasons for conducting research consisted of an interest in scientific problems or the research topic, a wish for personal development or intellectual stimulation. Students engaged in research reported lack of time, increased workload and less time to study as hindering factors.
Conclusions: Recruitment could be improved by offering improved and regular information, clarifying career paths, broadly announcing available projects, and creating new and expanding existing research programmes. The potential for recruitment of Gothenburg medical students to research is substantial, but students are hampered by lack of time, lack of supervisors and lack of information.
Keywords: Medical student; Physician; Recruitment; Research; Scientist.
Figures
References
-
- Stendahl O. Världsklass! Åtgärdsplan för den kliniska forskningen. SOU. 2008;Stockholm(7):1–271.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources